Spring Security 簡介
Spring Security 提供了對身份認證、授權和針對常見漏洞的保護的全面支持,可以輕鬆地集成到任何基於 Spring 的應用程序中。
主要就是提供了:
- 認證(Authentication):可以理解為登錄,驗證訪問者的身份。包括用户名密碼認證、手機號短信驗證碼認證、指紋識別認證、面容識別認證等等
- 授權(Authorization):授權發生在系統完成身份認證之後,最終會授予你訪問資源(如信息,文件,數據庫等等)的權限,授權決定了你訪問系統的能力以及達到的程度,比如只有拿到了操作用户的授權,才可以管理用户
- 漏洞保護:跨域、csrf 等防護
就我個人而言,以前對 Spring Security 的認識非常不清楚,所以這次從零開始一點一點的嘗試了一遍目前能遇到的大多數場景,下面是逐步探索 Spring Security 使用方法的整個過程,其中包括:
- Spring Boot 項目初始化
- 引入 Spring Security
- 內存用户登錄
- SecurityConfig
- UserDetailsService
- 接口權限限制
- 獲取認證信息
- 自定義登錄頁面
- 自定義登錄接口
- JWT 認證
- 多個 SecurityFilterChain
項目初始化
當前的 Spring Boot 版本是 3.1.2,Spring Security 的版本是 6.1.2
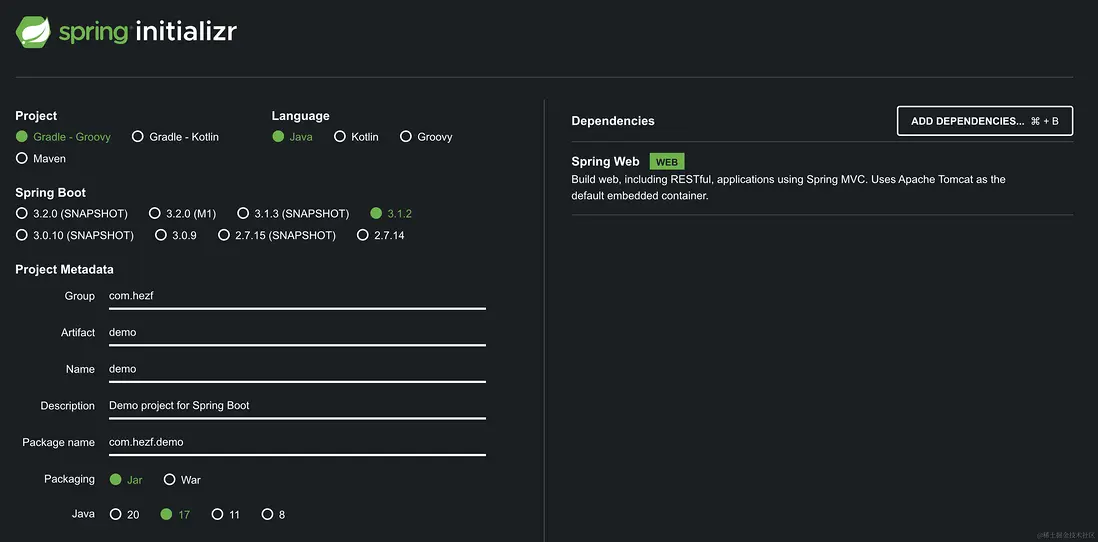
首先使用 Spring Initializr 添加 Spring Web 完成項目的創建
創建項目並下載打開後,新建一個 index 接口,這樣就可以啓動服務,訪問接口了
在src/main/java/com/hezf/demo/DemoApplication.java同級別目錄新建文件IndexController.java後,寫下第一個接口:
package com.example.hezf;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("/")
public String index() {
return "Hello Index!";
}
}
啓動項目,訪問本地 8080 接口:http://localhost:8080/,成功訪問到接口數據後,繼續下面的操作
引入 Spring Security
在 build.gradle 添加 implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-security' ,完成後需要 gradle 下載引入 security
下載後,重新啓動項目,繼續訪問 http://localhost:8080/
這時候發現跳轉到了一個登錄的頁面,這就表明 security 已經起作用了,不讓我們直接訪問接口了,接口被保護了起來
我們查看調試信息,會發現一條類似的信息Using generated security password: 9d53cf27-6c2b-4468-809a-247eb5d669da,把這個密碼和用户名user填上就可以繼續訪問剛才的接口
在密碼出現的下方有一條:This generated password is for development use only. Your security configuration must be updated before running your application in production.
這是告訴我們,這個用户和密碼只是在開發階段調試使用,生產環境不要這麼使用,接下來我們自定義用户和密碼。
內存用户登錄
上面的密碼使用起來太麻煩了,還是想辦法建幾個固定賬號吧,在src/main/java/com/hezf/demo/DemoApplication.java同級別目錄新建文件DefaultSecurityConfig.java:
package com.hezf.demo;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.provisioning.InMemoryUserDetailsManager;
@EnableWebSecurity
@Configuration
public class DefaultSecurityConfig {
@Bean
public UserDetailsService users() {
UserDetails user = User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder().username("user").password("password")
.roles("user").build();
return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(user);
}
}這時候重啓項目,發現控制枱沒有Using generated security password等信息出現了,可以使用 user 和 password 進行登錄,登錄後可以訪問 IndexController
這種內存用户可以快速的驗證登錄和一些權限控制,在項目中添加了 Spring Security 之後,默認對所有接口都開啓了訪問控制,只有已認證用户(已登錄)才可以訪問,接下來我們嘗試對 security 進行配置
SecurityConfig
在項目中添加 Spring Security後,必須登錄才能訪問接口,那麼怎麼把這個限制關掉?這時候可以使用 SecurityFilterChain,在 DefaultSecurityConfig 添加 SecurityFilterChain:
@EnableWebSecurity
@Configuration
public class DefaultSecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
return http.build();
}
@Bean
public UserDetailsService users() {
UserDetails user = User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder().username("user").password("password")
.roles("user").build();
return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(user);
}
}
當添加上面的配置重啓後,發現接口可以隨便訪問不需要登錄了,這是因為默認情況下,Spring Security 的接口保護、表單登錄被啓用。然而,只要提供 SecurityFilterChain 配置,就必須顯示啓用接口保護和表單登錄,否咋就不會生效。為了實現之前的接口保護和表單登錄,需要添加如下配置,啓用接口保護和表單登錄:
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeHttpRequests(authorize -> authorize.anyRequest().authenticated());
http.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults());
return http.build();
}第一句配置了訪問任何接口都需要認證,第二句是開啓表單登錄。如果想把接口保護去掉,那麼上面的配置改為http.authorizeHttpRequests(authorize -> authorize.anyRequest().permitAll()); 意思就是放行所有請求
UserDetailsService
前面我們使用了內存用户通過登錄獲取認證,來訪問接口。實際在開發過程中用户信息肯定是要持久化的,要存到數據庫中去,這時候最好實現一個 UserDetailsService 用來檢索用户名、密碼和其他屬性。
新建CustomUserDetailsService.java文件:
package com.hezf.demo;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import jakarta.annotation.PostConstruct;
@Service
public class CustomUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
private final Map<String, UserDetails> userRegistry = new HashMap<>();
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
UserDetails user = User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder().username("user").password("password")
.roles("user").build();
UserDetails user1 = User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder().username("user1").password("password")
.roles("user").build();
userRegistry.put("user", user);
userRegistry.put("user1", user1);
}
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
// 生產這裏是去數據庫查詢用户
UserDetails userDetails = userRegistry.get(username);
if (userDetails == null) {
throw new UsernameNotFoundException(username);
}
return userDetails;
}
}
DefaultSecurityConfig 修改一下,去掉 DefaultSecurityConfig 中的 UserDetailsService:
@EnableWebSecurity
@Configuration
public class DefaultSecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeHttpRequests(authorize -> authorize.anyRequest().authenticated());
http.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults());
return http.build();
}
}然後就可以用 user 和 user1 登錄了,以上是為了模擬真實的環境,一般在 loadUserByUsername 中進行數據庫查詢用户信息,然後返回裝填好信息的 UserDetails 進行認證
接口權限限制
在實際開發中,有的接口可以隨便訪問,比如 login 接口,有的接口必須登錄後才可以訪問,比如查詢當前用户信息的接口。有的接口可以管理其他用户,那就必須具有管理員權限才可以訪問。
接下來創建 3 種接口,一種不需要認證,一種已認證就行,最後一種需要某種權限才可以訪問。首先創建這 3 個接口:
@RestController
public class IndexController {
// 公開接口,可以隨便訪問
@RequestMapping("/public")
public String index() {
return "Hello Public!";
}
// 需要認證用户才可以訪問
@RequestMapping("/user")
public String user() {
return "Hello User!";
}
// 需要具有 ADMIN 權限才可以訪問
@RequestMapping("/admin")
public String admin() {
return "Hello Admin!";
}
}接下來配置 SecurityFilterChain:
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// @formatter:off
http.authorizeHttpRequests(authorize -> authorize
.requestMatchers("/public").permitAll() // /public 接口可以公開訪問
.requestMatchers("/admin").hasAuthority("ADMIN") // /admin 接口需要 ADMIN 權限
.anyRequest().authenticated()); // 其他的所以接口都需要認證才可以訪問
// @formatter:on
http.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults());
return http.build();
}然後準備用户數據:
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
UserDetails user = User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder().username("user").password("password")
.authorities("USER").build();
UserDetails admin = User.withDefaultPasswordEncoder().username("admin").password("password")
.authorities("ADMIN").build();
userRegistry.put("user", user);
userRegistry.put("admin", admin);
}重啓項目訪問 http://localhost:8080/public 成功訪問。接下來訪問 http://localhost:8080/user 會要求登錄,我們輸入 user 的用户名和密碼,成功訪問。繼續訪問 http://localhost:8080/admin 發現返回了 403 狀態嗎,告訴我們權限不正確,這時候清空下 cookie 重新使用 admin 登錄即可訪問。到此,我們實現了最小型的接口權限控制
獲取認證信息
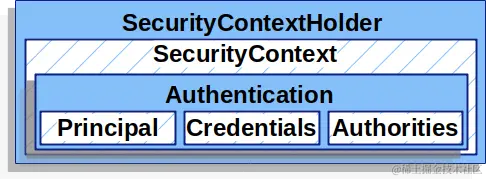
當用户第一次訪問受保護的接口時,會被重定向到登錄頁面,這時候後端服務會分配給用户一個會話 ID,存於 Cookies 中的 JSESSIONID。隨後的每次請求都會攜帶這個 Cookie,用於在接下來的會話中認證用户的身份。使用 SecurityContext ,可以獲取當前用户的認證信息,他們之間的關係可以看圖:
// 需要認證用户才可以訪問
@RequestMapping("/user")
public String user() {
// 靜態工具類 SecurityContextHolder 可以獲取當前的 SecurityContext 也就是上下文
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
// 認證,通過 authentication 可以獲取當前用户的一些信息
Authentication authentication = context.getAuthentication();
// 檢查是否已認證
System.out.println(authentication.isAuthenticated());
// 檢查用户詳情
UserDetails userDetail = (UserDetails) authentication.getPrincipal();
System.out.println(userDetail.getUsername());
System.out.println(userDetail.getPassword()); // 這裏是沒有密碼的
System.out.println(userDetail.getAuthorities());
return "Hello User!";
}上面的代碼只有在已認證的情況下才有效,認證的過程是 Spring Security 提供的登錄頁面和接口,下一步自己實現登錄過程
自定義登錄頁面
首先嚐試自定義登錄頁面,這樣可以直觀的看到前端頁面是怎麼提交用户名、密碼的
- 在
build.gradle添加依賴implementation "org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf" - 新建
src/main/resources/templates/login.html頁面:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="https://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Custom Log In Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Please Log In</h1>
<div th:if="${param.error}">Invalid username and password.</div>
<div th:if="${param.logout}">You have been logged out.</div>
<form th:action="@{/login}" method="post">
<div>
<input type="text" name="username" placeholder="Username" />
</div>
<div>
<input type="password" name="password" placeholder="Password" />
</div>
<input type="submit" value="Log in" />
</form>
</body>
</html>- 再配置文件
DefaultSecurityConfig:
http.formLogin(form -> form.loginPage("/login").permitAll());- 新建文件
src/main/java/com/hezf/demo/LoginController.java:
package com.hezf.demo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@GetMapping("/login")
String login() {
return "login";
}
}
這時候重啓項目,繼續訪問 /user ,會跳轉到我們自定義的登錄頁面,其他和以前的一樣。前面的配置修改是告訴 spring security 我們有自己的登錄頁面請求接口,LoginController 是為了返回這個自定義登錄頁面,上面添加的 thymeleaf 是為了解析登錄頁面 login.html
自定義登錄接口
前面我們自定義了登錄頁面,如果想自己定義登錄接口,就需要把默認的 formLogin 關掉,否則即使聲明瞭 POST 方法的 login 接口也沒用,登錄請求會被formLogin 攔截。所以我們直接註釋掉 formLogin 相關就可以了,這裏並不需要將 formLogin disabled 什麼的。有了默認的 SecurityFilterChain 後,默認 formLogin 就是關掉的
- 修改
DefaultSecurityConfig,這裏需要注意,需要把login接口開放出來,這裏新增了兩個異常處理,因為我想實現未登錄自動跳轉到登錄頁面
@EnableWebSecurity
@Configuration
public class DefaultSecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// @formatter:off
http.authorizeHttpRequests(authorize -> authorize
.requestMatchers("/public","/login").permitAll() // /public 接口可以公開訪問
.requestMatchers("/admin").hasAuthority("ADMIN") // /admin 接口需要 ADMIN 權限
.anyRequest().authenticated()); // 其他的所以接口都需要認證才可以訪問
// @formatter:on
// 設置異常的EntryPoint的處理
http.exceptionHandling(exceptions -> exceptions
// 未登錄
.authenticationEntryPoint(new MyAuthenticationEntryPoint())
// 權限不足
.accessDeniedHandler(new MyAccessDeniedHandler()));
// http.formLogin(Customizer.withDefaults());
// http.formLogin(form -> form.loginPage("/login").permitAll());
return http.build();
}
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManager(
AuthenticationConfiguration authenticationConfiguration) throws Exception {
return authenticationConfiguration.getAuthenticationManager();
}
}- 添加上面的兩個異常處理
MyAuthenticationEntryPoint和MyAccessDeniedHandler,分別是未登錄和未授權
package com.hezf.demo;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.web.AuthenticationEntryPoint;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
@Component
public class MyAuthenticationEntryPoint implements AuthenticationEntryPoint {
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.sendRedirect("login");
}
}package com.hezf.demo;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException;
import org.springframework.security.web.access.AccessDeniedHandler;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
@Component
public class MyAccessDeniedHandler implements AccessDeniedHandler {
private static ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED);
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
objectMapper.writeValue(response.getWriter(), "沒有對應的權限");
}
}
- 添加請求登錄接口,這裏完成了登錄信息的驗證,後續
http請求上下文的保存還有自動跳轉之前請求的鏈接
@PostMapping("/login")
void login(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@RequestParam("username") String username, @RequestParam("password") String password)
throws IOException, ServletException {
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken token =
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.unauthenticated(username, password);
// 通過前端發來的 username、password 進行認證,這裏會用到CustomUserDetailsService.loadUserByUsername
Authentication authentication = authenticationManager.authenticate(token);
// 設置空的上下文
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext();
// 設置認證信息
context.setAuthentication(authentication);
// 這句保證了隨後的請求都會有這個上下文,通過回話保持,在前端清理 cookie 之後也就失效了
securityContextRepository.saveContext(context, request, response);
// 檢查是否有之前請求的 URL,如果有就跳轉到之前的請求 URL 上去
SavedRequest savedRequest = new HttpSessionRequestCache().getRequest(request, response);
if (savedRequest != null) {
String targetUrl = savedRequest.getRedirectUrl();
response.sendRedirect(targetUrl);
} else {
response.sendRedirect("/public");
}
}運行項目,瀏覽器直接訪問 http://localhost:8080/user 會自動跳轉到自定義登錄頁面,輸入 user 用户名和密碼後,會自動跳轉回剛才訪問的 http://localhost:8080/user,這時候繼續訪問 http://localhost:8080/admin 會返回 "沒有對應的權限",到這裏我們就完成了:
- 自定義用户名密碼驗證的頁面和接口
- 未登錄自動跳轉到登錄頁面
- 登錄後自動跳轉到之前想訪問的接口
- 接口權限驗證
JWT 認證
上面我們完成了自定義的接口,自動跳轉等等。。。但是現在更普遍的是前後端分離的項目,這樣更容易擴展應用場景。下面來實現登錄後頒發 jwt,以及通過 jwt 來進行認證和權限判斷
- 引入所需的
jwt庫
// jwt相關
implementation 'io.jsonwebtoken:jjwt-api:0.11.5'
runtimeOnly 'io.jsonwebtoken:jjwt-impl:0.11.5'
runtimeOnly 'io.jsonwebtoken:jjwt-jackson:0.11.5'- 添加
jwt的默認配置
在 src/main/resources 下刪除原來的 application.properties,並且創建文件 src/main/resources/application.yml,填入以下內容:
jwt:
# 60*60*1
expire: 3600
# secret: 秘鑰(普通字符串)
secret: pa1R0cHM6hyGf8Hyb7D34LKJ8b4gldC91LzM2ODE4Njg- 添加頒發、解析、認證
jwt等工具類
新建 src/main/java/com/hezf/demo/JWTProvider.java 文件,這個類的作用是:
1、生成 jwt(在登錄的時候生成,根據 username 和對應的權限列表)
2、檢驗 jwt 有效性和提取 jwt 中的認證信息(使用 jwt 訪問接口的時候)
@Component
public class JWTProvider {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JWTProvider.class);
private static final String AUTHORITIES_KEY = "permissions";
private static SecretKey secretKey;
@Value("${jwt.secret}")
public void setJwtSecret(String secret) {
secretKey = Keys.hmacShaKeyFor(Decoders.BASE64.decode(secret));
}
private static int jwtExpirationInMs;
@Value("${jwt.expire}")
public void setJwtExpirationInMs(int expire) {
jwtExpirationInMs = expire;
}
// generate JWT token
public static String generateToken(Authentication authentication) {
long currentTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
Date expirationDate = new Date(currentTimeMillis + jwtExpirationInMs * 1000);
String scope = authentication.getAuthorities().stream().map(GrantedAuthority::getAuthority)
.collect(Collectors.joining(","));
Claims claims = Jwts.claims().setSubject(authentication.getName());
claims.put(AUTHORITIES_KEY, scope);
return Jwts.builder().setClaims(claims).setExpiration(expirationDate)
.signWith(secretKey, SignatureAlgorithm.HS256).compact();
}
public static Authentication getAuthentication(String token) {
Claims claims =
Jwts.parserBuilder().setSigningKey(secretKey).build().parseClaimsJws(token).getBody();
// 從jwt獲取用户權限列
String permissionString = (String) claims.get(AUTHORITIES_KEY);
List<SimpleGrantedAuthority> authorities =
permissionString.isBlank() ? new ArrayList<SimpleGrantedAuthority>()
: Arrays.stream(permissionString.split(",")).map(SimpleGrantedAuthority::new)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 獲取 username
String username = claims.getSubject();
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, null, authorities);
}
// validate Jwt token
public static boolean validateToken(String token) {
try {
Jwts.parserBuilder().setSigningKey(secretKey).build().parse(token);
return true;
} catch (MalformedJwtException e) {
logger.error("Invalid JWT token: {}", e.getMessage());
} catch (ExpiredJwtException e) {
logger.error("JWT token is expired: {}", e.getMessage());
} catch (UnsupportedJwtException e) {
logger.error("JWT token is unsupported: {}", e.getMessage());
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
logger.error("JWT claims string is empty: {}", e.getMessage());
}
return false;
}
}
新建src/main/java/com/hezf/demo/JWTFilter.java文件,這個類的作用是:
1、除了登錄接口以外,其他接口在進入接口之前,都需要經過 JWTFilter 的處理
2、驗證 jwt 的合法性和有效期等
3、提取 jwt 中的 username 和 權限,生成 Authentication 存到 security 上下文
4、security 上下文中有了 Authentication ,那就代表着已認證,後續也可以在接口中使用 Authentication 中的信息
@Component
public class JWTFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JWTFilter.class);
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 這部分出錯後,直接返回401,不再走後面的filter
try {
// 從請求頭中獲取jwt
String jwt = getJwtFromRequest(request);
// 校驗 jwt 是否有效,包含了過期的驗證
if (StringUtils.hasText(jwt) && JWTProvider.validateToken(jwt)) {
// 通過 jwt 獲取認證信息
Authentication authentication = JWTProvider.getAuthentication(jwt);
// 將認證信息存入 Security 上下文中,可以取出來使用,也代表着已認證
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
LOGGER.error("Could not set user authentication in security context", ex);
}
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
private String getJwtFromRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
String bearerToken = request.getHeader("Authorization");
if (StringUtils.hasText(bearerToken) && bearerToken.startsWith("Bearer ")) {
return bearerToken.substring(7, bearerToken.length());
}
return null;
}
}
- 修改
springsecurity配置,因為使用了jwt進行認證,所以不需要csrf保護了
// 關閉 csrf 保護
http.csrf(csrf -> csrf.disable());
// 在過濾器鏈中添加 JWTFilter
http.addFilterBefore(new JWTFilter(), LogoutFilter.class);- 重寫登錄接口,像上次一樣,提取
username和password進行認證,認證成功以後返回jwt,失敗的話返回錯誤信息
class LoginRequest {
private String username;
private String password;
public String getUsername() {
return this.username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return this.password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
@RestController
public class LoginController {
@Autowired
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
@PostMapping("/login")
public Map<String, Object> login(@RequestBody LoginRequest login) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
try {
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken token = UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
.unauthenticated(login.getUsername(), login.getPassword());
Authentication authentication = authenticationManager.authenticate(token);
String jwt = JWTProvider.generateToken(authentication);
map.put("jwt", jwt);
} catch (BadCredentialsException ex) {
map.put("error", ex.getMessage());
}
return map;
}
}
上面的 authenticationManager.authenticate(token); 這句會完成用户名密碼的認證工作,會調用 CustomUserDetailsService.loadUserByUsername 後進行對比,失敗後返回錯誤信息
- 測試接口
使用 postman 等測試工具,發起 post 請求,格式為 json
- 當發送的用户名密碼錯誤的時候,返回
{"error":"用户名或密碼錯誤"} - 正確的話返回
{"jwt": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJzdWIiOiJ1c2VyIiwicGVybWlzc2lvbnMiOiJVU0VSIiwiZXhwIjoxNjk1MzUxODAyfQ._cNekfYovmnjWKBaKVCiErzu76q-Aj3gZhUsDiITzAA"} - 在 header 中添加 Authorization,並填寫值
Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJzdWIiOiJ1c2VyIiwicGVybWlzc2lvbnMiOiJVU0VSIiwiZXhwIjoxNjk1MzUxODAyfQ._cNekfYovmnjWKBaKVCiErzu76q-Aj3gZhUsDiITzAA,後面的一長串就是上一步得到的 jwt, - 發起 GET 請求
http://127.0.0.1:8080/user,這時候得到Hello User! - 繼續發起 GET 請求
http://127.0.0.1:8080/user,這時候得到"沒有對應的權限"
多個 SecurityFilterChain
接下來來看一個更加複雜的情況,如何在已經使用會話做認證的情況下,添加 JWT 認證做 API 接口管理?也就是説,需要同時支持兩種認證:
- 會話認證:訪問需要認證的頁面,沒有認證的情況下自動跳轉到登錄頁面,登錄成功後自動跳回剛才訪問的頁面
JWT認證:支持通過API接口進行登錄和訪問API接口
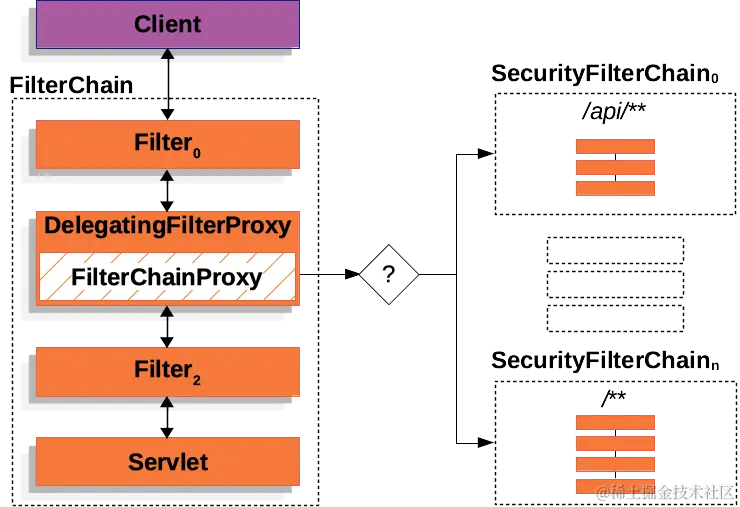
答案是同時可以設置多個 SecurityFilterChain,然後根據訪問不同的 URL 確定使用哪個 SecurityFilterChain,只有第一個匹配的 SecurityFilterChain 被調用,如下所示:
如果請求的 URL 是 /api/user/,它首先與 /api/** 的 SecurityFilterChain0 模式匹配,所以只有 SecurityFilterChain0 被調用,儘管它也與 SecurityFilterChain1 匹配,但是隻調用第一個匹配的
- 首先準備好兩套登錄接口
// src/main/java/com/hezf/demo/jwt/JWTLoginController.java
class LoginRequest {
private String username;
private String password;
public String getUsername() {
return this.username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return this.password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class JWTLoginController {
@Autowired
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
@PostMapping("/login")
public Map<String, Object> login(@RequestBody LoginRequest login) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
try {
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken token = UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
.unauthenticated(login.getUsername(), login.getPassword());
Authentication authentication = authenticationManager.authenticate(token);
String jwt = JWTProvider.generateToken(authentication);
map.put("jwt", jwt);
} catch (BadCredentialsException ex) {
map.put("error", ex.getMessage());
}
return map;
}
}// src/main/java/com/hezf/demo/session/SessionLoginController.java
@Controller
public class SessionLoginController {
@Autowired
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
private SecurityContextRepository securityContextRepository =
new HttpSessionSecurityContextRepository();
@GetMapping("/login")
String login() {
return "login";
}
@PostMapping("/login")
void login(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@RequestParam("username") String username, @RequestParam("password") String password)
throws IOException, ServletException {
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken token =
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.unauthenticated(username, password);
// 通過前端發來的 username、password 進行認證,這裏會用到CustomUserDetailsService.loadUserByUsername
Authentication authentication = authenticationManager.authenticate(token);
// 設置空的上下文
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.createEmptyContext();
// 設置認證信息
context.setAuthentication(authentication);
// 這句保證了隨後的請求都會有這個上下文,通過回話保持,在前端清理 cookie 之後也就失效了
securityContextRepository.saveContext(context, request, response);
// 檢查是否有之前請求的 URL,如果有就跳轉到之前的請求 URL 上去
SavedRequest savedRequest = new HttpSessionRequestCache().getRequest(request, response);
if (savedRequest != null) {
String targetUrl = savedRequest.getRedirectUrl();
response.sendRedirect(targetUrl);
} else {
response.sendRedirect("/public");
}
}
}
- 然後準備好兩套未認證和權限錯誤的處理,這部分代碼不貼了,可以自行查找:
// JWT
src/main/java/com/hezf/demo/jwt/JWTAuthenticationEntryPoint.java
src/main/java/com/hezf/demo/jwt/JWTAccessDeniedHandler.java
// session
src/main/java/com/hezf/demo/session/SessionAuthenticationEntryPoint.java
src/main/java/com/hezf/demo/session/SessionAccessDeniedHandler.java- 繼續準備好兩套 user 和 admin 的接口
src/main/java/com/hezf/demo/jwt/JWTController.java
src/main/java/com/hezf/demo/session/SessionController.javaJWT所需的JWTProvider和JWTFilter內容不變- 最後是配置
SecurityFilterChain
@EnableWebSecurity
@Configuration
public class DefaultSecurityConfig {
@Bean
@Order(0) // 最高優先級,這裏處理的都是以 /api/** 開頭的接口,使用 jwt 做認證
public SecurityFilterChain jwtFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// @formatter:off
http.securityMatcher("/api/**").authorizeHttpRequests(authorize -> authorize
.requestMatchers("/api/login").permitAll() // /public 接口可以公開訪問
.requestMatchers("/api/admin").hasAuthority("ADMIN") // /admin 接口需要 ADMIN 權限
.anyRequest().authenticated()); // 其他的所以接口都需要認證才可以訪問
// @formatter:on
// 設置異常的EntryPoint的處理
http.exceptionHandling(exceptions -> exceptions
// 未登錄
.authenticationEntryPoint(new JWTAuthenticationEntryPoint())
// 權限不足
.accessDeniedHandler(new JWTAccessDeniedHandler()));
// 關閉 csrf 保護
http.csrf(csrf -> csrf.disable());
// 在過濾器鏈中添加 JWTFilter
http.addFilterBefore(new JWTFilter(), LogoutFilter.class);
return http.build();
}
@Bean
@Order(1) // 次高優先級,處理會話認證
public SecurityFilterChain sessionFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
// @formatter:off
http.authorizeHttpRequests(authorize -> authorize
.requestMatchers("/public","/login").permitAll() // /public 接口可以公開訪問
.requestMatchers("/admin").hasAuthority("ADMIN") // /admin 接口需要 ADMIN 權限
.anyRequest().authenticated()); // 其他的所以接口都需要認證才可以訪問
// @formatter:on
// 設置異常的EntryPoint的處理
http.exceptionHandling(exceptions -> exceptions
// 未登錄
.authenticationEntryPoint(new SessionAuthenticationEntryPoint())
// 權限不足
.accessDeniedHandler(new SessionAccessDeniedHandler()));
return http.build();
}
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManager(
AuthenticationConfiguration authenticationConfiguration) throws Exception {
return authenticationConfiguration.getAuthenticationManager();
}
}最後的結構是這樣的,也可以查看源碼:
最後我們進行測試,首先是會話認證:
- 啓動項目後,在瀏覽器訪問
http://localhost:8080/user,會自動跳轉到http://localhost:8080/login - 輸入用户名、密碼後,會自動跳回
http://localhost:8080/user,並顯示Hello User! - 最後,將瀏覽器 訪問地址改為
http://localhost:8080/admin,會顯示沒有對應的權限,會話認證基本驗證完成
接下來測試 JWT 認證:
- 使用調試工具 POST
http://localhost:8080/api/login,body 裏面填寫{"username": "user","password": "password"} - 登錄成功後,獲取返回值,複製 jwt 的值,在 Header 中添加
Authorization: Bearer jwt的值 - 訪問 GET
http://localhost:8080/api/user,可以正常訪問接口,然後攜帶相同的 Header 繼續訪問http://localhost:8080/api/admin, 返回沒有對應的權限
以上説明,兩個 SecurityFilterChain 都在運行,並且都是獨立的,互不影響。這樣做的好處是可以給單獨某一些 API 設置獨有的認證授權,和其他的互不影響。
總結
好了,目前完成了較複雜的 Spring Security 配置、認證和權限驗證。整個過程下來之後,認識了一些Spring Security 的默認規則和常用的方法套路,大部分的場景都可以覆蓋。根據以上內容可實現基於 RBAC 的訪問控制,這部分內容可以參考以前的項目,一般的項目基本上夠用了。
本文源碼