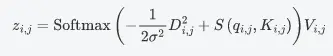我們社區有新的技術分享小夥伴啦🎉🎉🎉
熱烈歡迎👏
作為一名合格的搬運工,我必須做點事情表達我的喜悦之情:搬運~搬運~立即搬運~
文章來源 | 恆源雲社區
原文地址 | 新的混合Transformer模塊(MTM)
原文作者 | 咚咚
摘要
| 存在問題 | 雖然U-Net在醫學圖像分割方面取得了巨大的成功,但它缺乏對長期依賴關係進行顯式建模的能力。視覺Transformer由於其固有的通過自注意(SA)捕捉長程相關性的能力,近年來成為一種可替代的分割結構。 |
|---|---|
| 存在問題 | 然而,Transformer通常依賴於大規模的預訓練,具有較高的計算複雜度。此外,SA只能在單個樣本中建模self-affinities,忽略了整個數據集的潛在相關性 |
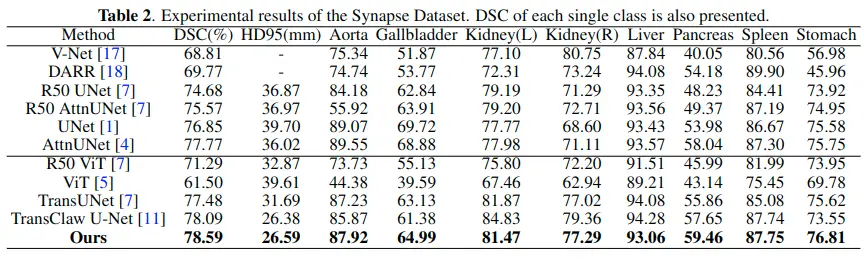
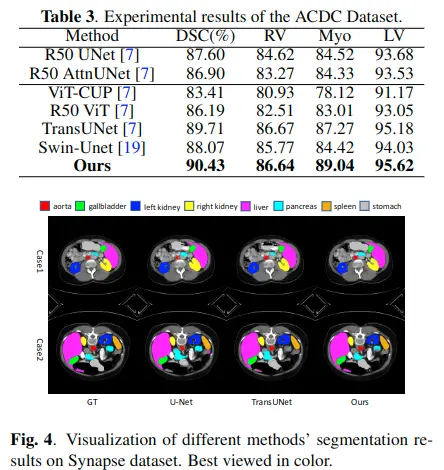
| 論文方法 | 提出了一種新的混合Transformer模塊(MTM),用於同時進行inter-affinities學習和intra-affinities學習。MTM首先通過局部-全局高斯加權自注意(LGG-SA)有效地計算窗口內部affinities。然後,通過外部注意挖掘數據樣本之間的聯繫。利用MTM算法,構造了一種用於醫學圖像分割的MT-UNet模型 |
Method
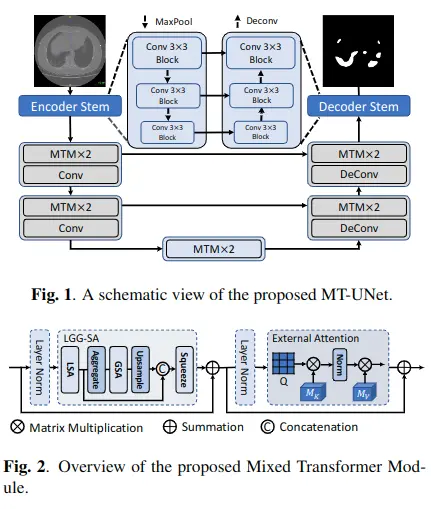
如圖1所示。該網絡基於編碼器-解碼器結構
- 為了降低計算成本,MTMs只對空間大小較小的深層使用,
- 淺層仍然使用經典的卷積運算。這是因為淺層主要關注局部信息,包含更多高分辨率的細節。
MTM
如圖2所示。MTM主要由LGG-SA和EA組成。
LGG-SA用於對不同粒度的短期和長期依賴進行建模,而EA用於挖掘樣本間的相關性。
該模塊是為了替代原來的Transformer編碼器,以提高其在視覺任務上的性能和降低時間複雜度
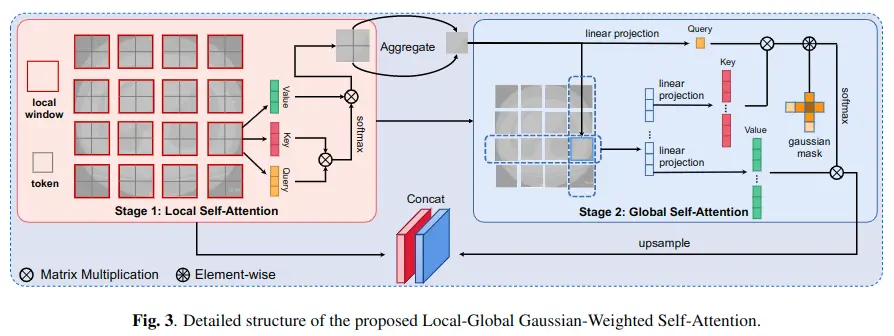
LGG-SA(Local-Global Gaussian-Weighted Self-Attention)
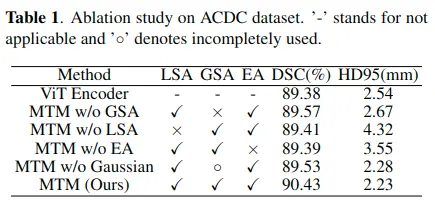
傳統的SA模塊對所有tokens賦予相同的關注度,而LGG -SA則不同,利用local-global自注意力和高斯mask使其可以更專注於鄰近區域。實驗證明,該方法可以提高模型的性能,節省計算資源。該模塊的詳細設計如圖3所示
local-global自注意力
在計算機視覺中,鄰近區域之間的相關性往往比遙遠區域之間的相關性更重要,在計算注意圖時,不需要為更遠的區域花費相同的代價。
因此,提出local-global自注意力。
- 上圖stage1中的每個局部窗口中含有四個token,local SA計算每個窗口內的內在affinities。
- 每個窗口中的token被aggregate聚合為一個全局token ,表示窗口的主要信息。對於聚合函數,輕量級動態卷積(Lightweight Dynamic convolution, LDConv)的性能最好。
- 在得到下采樣的整個特徵圖後,可以以更少的開銷執行global SA(上圖stage2)。
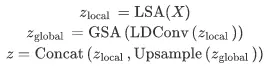
其中\( X \in R^{H \times W \times C} \)
其中,stage1中的局部窗口自注意力代碼如下:
class WinAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, configs, dim):
super(WinAttention, self).__init__()
self.window_size = configs["win_size"]
self.attention = Attention(dim, configs)
def forward(self, x):
b, n, c = x.shape
h, w = int(np.sqrt(n)), int(np.sqrt(n))
x = x.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous().view(b, c, h, w)
if h % self.window_size != 0:
right_size = h + self.window_size - h % self.window_size
new_x = torch.zeros((b, c, right_size, right_size))
new_x[:, :, 0:x.shape[2], 0:x.shape[3]] = x[:]
new_x[:, :, x.shape[2]:,
x.shape[3]:] = x[:, :, (x.shape[2] - right_size):,
(x.shape[3] - right_size):]
x = new_x
b, c, h, w = x.shape
x = x.view(b, c, h // self.window_size, self.window_size,
w // self.window_size, self.window_size)
x = x.permute(0, 2, 4, 3, 5,
1).contiguous().view(b, h // self.window_size,
w // self.window_size,
self.window_size * self.window_size,
c).cuda()
x = self.attention(x) # (b, p, p, win, c) 對局部窗口內的tokens進行自注意力計算
return x聚合函數代碼如下
class DlightConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, configs):
super(DlightConv, self).__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(dim, configs["win_size"] * configs["win_size"])
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, x): # (b, p, p, win, c)
h = x
avg_x = torch.mean(x, dim=-2) # (b, p, p, c)
x_prob = self.softmax(self.linear(avg_x)) # (b, p, p, win)
x = torch.mul(h,
x_prob.unsqueeze(-1)) # (b, p, p, win, c)
x = torch.sum(x, dim=-2) # (b, p, p, c)
return xGaussian-Weighted Axial Attention
與使用原始SA的LSA不同,提出了高斯加權軸向注意(GWAA)的方法。GWAA通過一個可學習的高斯矩陣增強了相鄰區域的感知全權重,同時由於具有軸向注意力而降低了時間複雜度。
- 上圖中stage2中特徵圖的第三行第三列特徵進行linear projection得到\( q_{i, j} \)
- 將該特徵點所在行和列的所有特徵分別進行linear projection得到\( K_{i, j} \)
和\( V_{i, j} \) - 將該特徵點與所有的K和V的歐式距離定義為\( D_{i, j} \)
最終的高斯加權軸向注意力輸出結果為
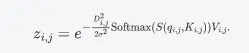
並簡化為
軸向注意力代碼如下:
class Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, configs, axial=False):
super(Attention, self).__init__()
self.axial = axial
self.dim = dim
self.num_head = configs["head"]
self.attention_head_size = int(self.dim / configs["head"])
self.all_head_size = self.num_head * self.attention_head_size
self.query_layer = nn.Linear(self.dim, self.all_head_size)
self.key_layer = nn.Linear(self.dim, self.all_head_size)
self.value_layer = nn.Linear(self.dim, self.all_head_size)
self.out = nn.Linear(self.dim, self.dim)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def transpose_for_scores(self, x):
new_x_shape = x.size()[:-1] + (self.num_head, self.attention_head_size)
x = x.view(*new_x_shape)
return x
def forward(self, x):
# first row and col attention
if self.axial:
# x: (b, p, p, c)
# row attention (single head attention)
b, h, w, c = x.shape
mixed_query_layer = self.query_layer(x)
mixed_key_layer = self.key_layer(x)
mixed_value_layer = self.value_layer(x)
query_layer_x = mixed_query_layer.view(b * h, w, -1)
key_layer_x = mixed_key_layer.view(b * h, w, -1).transpose(-1, -2) # (b*h, -1, w)
attention_scores_x = torch.matmul(query_layer_x,
key_layer_x) # (b*h, w, w)
attention_scores_x = attention_scores_x.view(b, -1, w,
w) # (b, h, w, w)
# col attention (single head attention)
query_layer_y = mixed_query_layer.permute(0, 2, 1,
3).contiguous().view(
b * w, h, -1)
key_layer_y = mixed_key_layer.permute(
0, 2, 1, 3).contiguous().view(b * w, h, -1).transpose(-1, -2) # (b*w, -1, h)
attention_scores_y = torch.matmul(query_layer_y,
key_layer_y) # (b*w, h, h)
attention_scores_y = attention_scores_y.view(b, -1, h,
h) # (b, w, h, h)
return attention_scores_x, attention_scores_y, mixed_value_layer
else:
mixed_query_layer = self.query_layer(x)
mixed_key_layer = self.key_layer(x)
mixed_value_layer = self.value_layer(x)
query_layer = self.transpose_for_scores(mixed_query_layer).permute(
0, 1, 2, 4, 3, 5).contiguous() # (b, p, p, head, n, c)
key_layer = self.transpose_for_scores(mixed_key_layer).permute(
0, 1, 2, 4, 3, 5).contiguous()
value_layer = self.transpose_for_scores(mixed_value_layer).permute(
0, 1, 2, 4, 3, 5).contiguous()
attention_scores = torch.matmul(query_layer,
key_layer.transpose(-1, -2))
attention_scores = attention_scores / math.sqrt(
self.attention_head_size)
atten_probs = self.softmax(attention_scores)
context_layer = torch.matmul(
atten_probs, value_layer) # (b, p, p, head, win, h)
context_layer = context_layer.permute(0, 1, 2, 4, 3,
5).contiguous()
new_context_layer_shape = context_layer.size()[:-2] + (
self.all_head_size, )
context_layer = context_layer.view(*new_context_layer_shape)
attention_output = self.out(context_layer)
return attention_output高斯加權代碼如下:
class GaussianTrans(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(GaussianTrans, self).__init__()
self.bias = nn.Parameter(-torch.abs(torch.randn(1)))
self.shift = nn.Parameter(torch.abs(torch.randn(1)))
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, x):
x, atten_x_full, atten_y_full, value_full = x #x(b, h, w, c) atten_x_full(b, h, w, w) atten_y_full(b, w, h, h) value_full(b, h, w, c)
new_value_full = torch.zeros_like(value_full)
for r in range(x.shape[1]): # row
for c in range(x.shape[2]): # col
atten_x = atten_x_full[:, r, c, :] # (b, w)
atten_y = atten_y_full[:, c, r, :] # (b, h)
dis_x = torch.tensor([(h - c)**2 for h in range(x.shape[2])
]).cuda() # (b, w)
dis_y = torch.tensor([(w - r)**2 for w in range(x.shape[1])
]).cuda() # (b, h)
dis_x = -(self.shift * dis_x + self.bias).cuda()
dis_y = -(self.shift * dis_y + self.bias).cuda()
atten_x = self.softmax(dis_x + atten_x)
atten_y = self.softmax(dis_y + atten_y)
new_value_full[:, r, c, :] = torch.sum(
atten_x.unsqueeze(dim=-1) * value_full[:, r, :, :] +
atten_y.unsqueeze(dim=-1) * value_full[:, :, c, :],
dim=-2)
return new_value_fulllocal-global自注意力完整代碼如下:
class CSAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, configs):
super(CSAttention, self).__init__()
self.win_atten = WinAttention(configs, dim)
self.dlightconv = DlightConv(dim, configs)
self.global_atten = Attention(dim, configs, axial=True)
self.gaussiantrans = GaussianTrans()
#self.conv = nn.Conv2d(dim, dim, 3, padding=1)
#self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(2)
self.up = nn.UpsamplingBilinear2d(scale_factor=4)
self.queeze = nn.Conv2d(2 * dim, dim, 1)
def forward(self, x):
'''
:param x: size(b, n, c)
:return:
'''
origin_size = x.shape
_, origin_h, origin_w, _ = origin_size[0], int(np.sqrt(
origin_size[1])), int(np.sqrt(origin_size[1])), origin_size[2]
x = self.win_atten(x) # (b, p, p, win, c)
b, p, p, win, c = x.shape
h = x.view(b, p, p, int(np.sqrt(win)), int(np.sqrt(win)),
c).permute(0, 1, 3, 2, 4, 5).contiguous()
h = h.view(b, p * int(np.sqrt(win)), p * int(np.sqrt(win)),
c).permute(0, 3, 1, 2).contiguous() # (b, c, h, w)
x = self.dlightconv(x) # (b, p, p, c)
atten_x, atten_y, mixed_value = self.global_atten(
x) # (b, h, w, w) (b, w, h, h) (b, h, w, c)這裏的h w就是p
gaussian_input = (x, atten_x, atten_y, mixed_value)
x = self.gaussiantrans(gaussian_input) # (b, h, w, c)
x = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2).contiguous() # (b, c, h, w)
x = self.up(x)
x = self.queeze(torch.cat((x, h), dim=1)).permute(0, 2, 3,
1).contiguous()
x = x[:, :origin_h, :origin_w, :].contiguous()
x = x.view(b, -1, c)
return xEA
外部注意(External Attention, EA),是用於解決SA無法利用不同輸入數據樣本之間關係的問題。
與使用每個樣本自己的線性變換來計算注意分數的自我注意不同,在EA中,所有的數據樣本共享兩個記憶單元MK和MV(如圖2所示),描述了整個數據集的最重要信息。
EA代碼如下:
class MEAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, configs):
super(MEAttention, self).__init__()
self.num_heads = configs["head"]
self.coef = 4
self.query_liner = nn.Linear(dim, dim * self.coef)
self.num_heads = self.coef * self.num_heads
self.k = 256 // self.coef
self.linear_0 = nn.Linear(dim * self.coef // self.num_heads, self.k)
self.linear_1 = nn.Linear(self.k, dim * self.coef // self.num_heads)
self.proj = nn.Linear(dim * self.coef, dim)
def forward(self, x):
B, N, C = x.shape
x = self.query_liner(x) # (b, n, 4c)
x = x.view(B, N, self.num_heads, -1).permute(0, 2, 1,
3) # (b, h, n, 4c/h)
attn = self.linear_0(x) # (b, h, n, 256/4)
attn = attn.softmax(dim=-2) # (b, h, 256/4)
attn = attn / (1e-9 + attn.sum(dim=-1, keepdim=True)) # (b, h, 256/4)
x = self.linear_1(attn).permute(0, 2, 1, 3).reshape(B, N, -1)
x = self.proj(x)
return xEXPERIMENTS