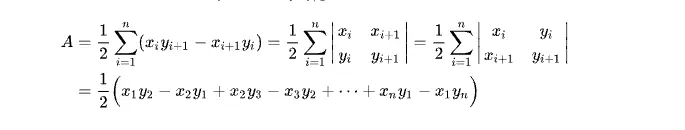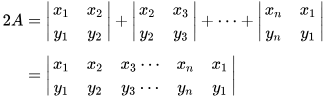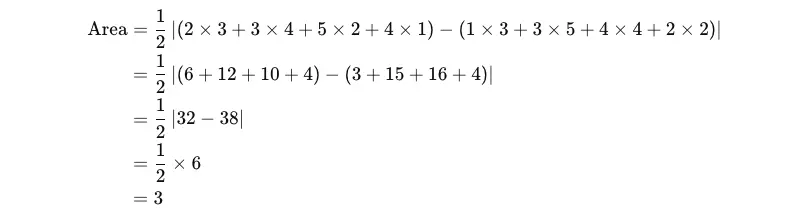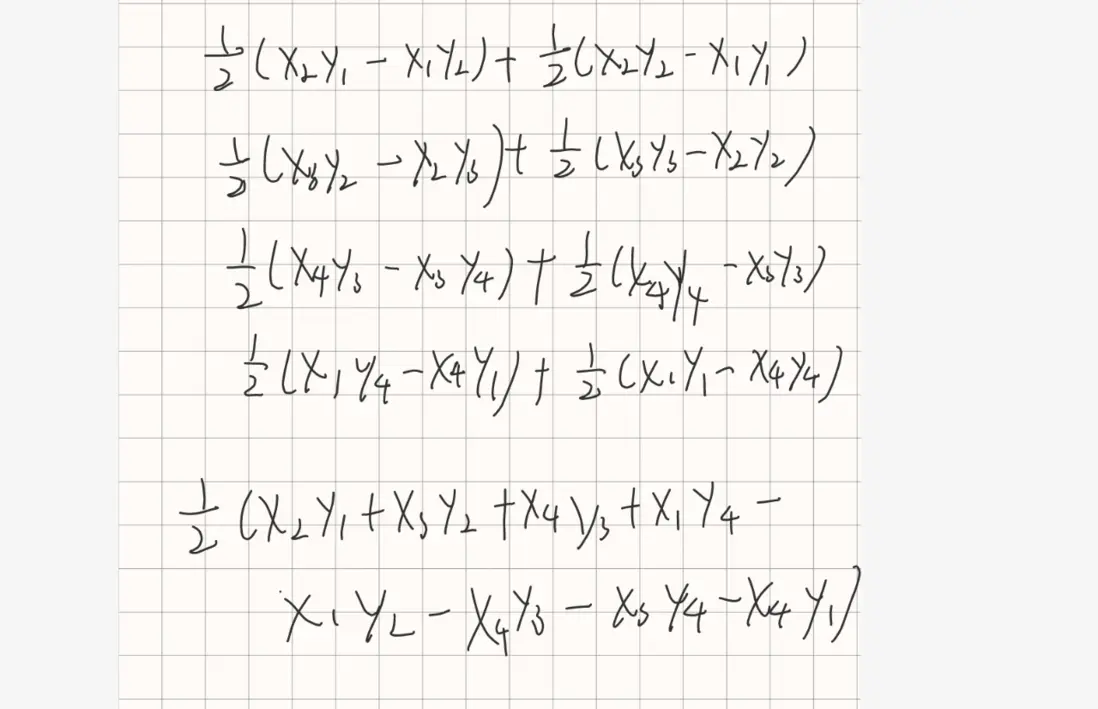前言
當前有一個需求,在之前進行對進行發票設別標註的時候遇到的痛點,那就是需要用户下載指定環境,而且有很多小毛病,無疑是增加了工作量。在這個基礎上,就決定自己在web進行圖像標註,由web端進行畫框進行標圖進行保存四個座標,根據之後再根據四個座標進行圖像切片。基於此就有了這個文章,本文將介紹如何使用高斯面積公式(也稱為Shoelace公式)計算多邊形的有向面積,並結合圖像處理技術對圖像進行旋轉裁剪。
裁剪的圖片
實現的效果
實現步驟
- 計算多邊形的有向面積:利用高斯面積公式計算多邊形的有向面積。如果面積為負,説明頂點是按逆時針順序排列的,需要進行調整以確保順時針順序。
- 計算裁剪圖像的寬度和高度:根據調整後的頂點座標,計算旋轉裁剪後圖像的寬度和高度。
- 執行旋轉裁剪:使用計算得到的寬度和高度,對圖像進行旋轉裁剪。
計算多邊形的有向面積
d = 0.0
# 使用高斯面積公式計算多邊形的有向面積
for index in range(-1, 3):
d += -0.5 * (points[index + 1][1] + points[index][1]) * (
points[index + 1][0] - points[index][0])
# 如果面積為負,交換點的位置以確保順時針順序
if d < 0:
tmp = np.array(points)
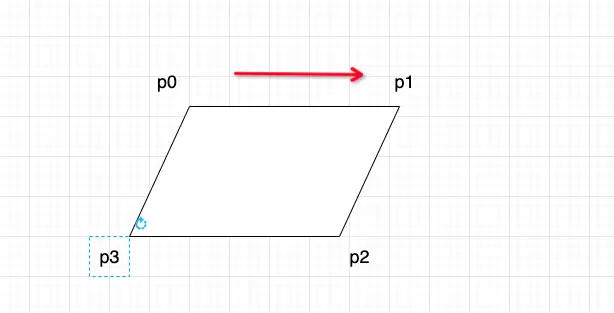
points[1], points[3] = tmp[3], tmp[1]為什麼要確保為順時針,這是因為我們需要計算固定長和寬
順時針的情況
逆時針的情況
高斯面積公式
- Shoelace公式(也稱為高斯面積公式或鞋帶公式)是一個用於計算二維平面上簡單多邊形面積的算法。這個公式的基本思想是將多邊形的頂點視為平面上的點,並通過這些點的座標來計算多邊形的面積。
高斯面積公式
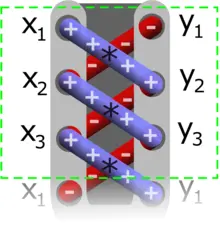
鞋帶公式
長的很像鞋帶
為什麼叫做鞋帶公式,這是因為在計算的過程很像鞋帶一樣纏繞着,
鞋帶公式是這樣子算的:
鞋帶公式多邊形面積計算
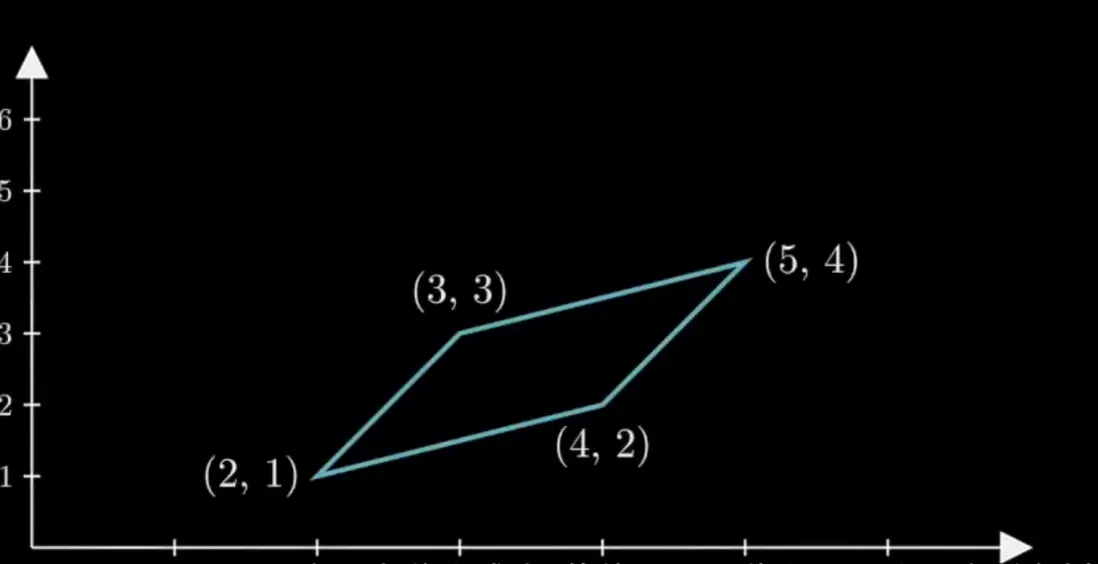
比如一個多邊形(四角形),
P1(x1,y2)=(2,1),P2(x2,y2)=(3, 3),P3(x3,y3)=(5, 4),P4(x4,y4)=(4, 2)
可得面積:
為什麼要加絕對值,這就是涉及到高斯面積公式的推理過程,結合這個多邊形案例
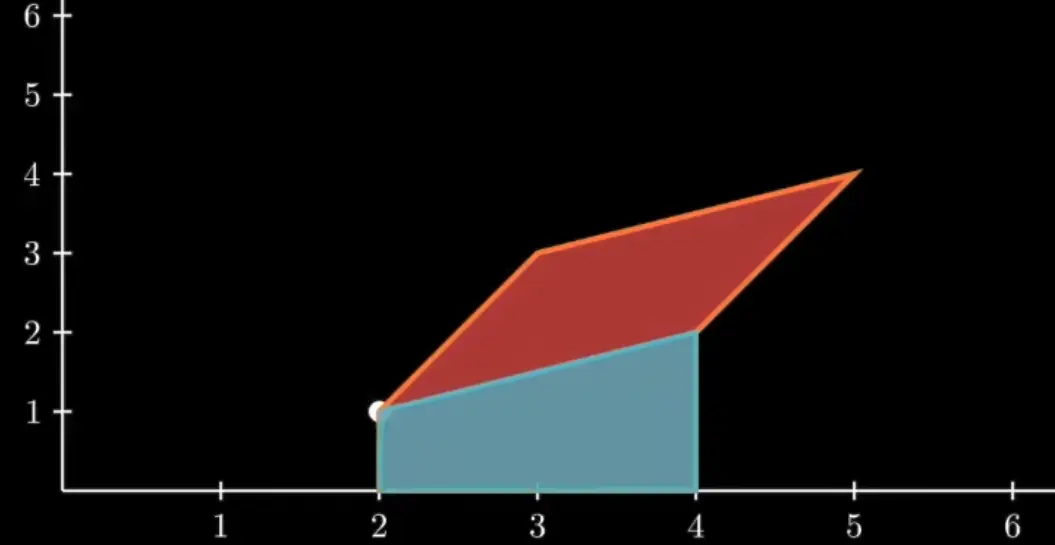
梯形公式
計算P1到P2的面積
(x1, y1) = (2, 1) (x2, y2) = (3, 3)
2/(x2y1 - x1y2) + 2/(x2y2-x1y1)
area = 2
計算P2 到 P3梯形面積
(x2, y2) = (3, 3) (x3, y3) = (5, 4)
2/(x3y2 - x2y3) + 2/(x3y3-x2y2)
area = 7
計算P3 到 P4 梯形面積
這裏發現當前的x4-x3 當x3大於x4時,計算的梯形面積為負數
(x3, y3) = (5, 4) (x4, y4) = (4, 2)
2/(x4y3 - x3y4) + 2/(x4y4-x3y3)
are = -3
計算x4y4 x1y1 梯形面積
這裏發現當前的x1-x4 當x4大於x1時,計算的梯形面積為負數
(x1, y1) = (2, 1) (x4, y4) = (4, 2)
2/(x1y4 - x4y1) + 2/(x1y1-x4y4)
area = -3
最後相加可得高斯面積公式
根據面積相加可得
area1 + area2 + area3 + area4 = area
2 + 7 - 3 -3 = 3
使用勾股定理計算圖像長和寬
[0, 0],[4, 0],[4, 3], [0, 3]
# 計算裁剪圖像的寬度
img_crop_width = int(
max(
# 勾股定理
np.linalg.norm(points[0] - points[1]), # 距離 (0,0) 到 (4,0)
np.linalg.norm(points[2] - points[3]))) # 距離 (4,3) 到 (0,3)
# 計算裁剪圖像的高度
img_crop_height = int(
max(
np.linalg.norm(points[0] - points[3]), # 距離 (0,0) 到 (0,3)
np.linalg.norm(points[1] - points[2]))) # 距離 (4,0) 到 (4,3)
pts_std = np.float32([[0, 0], [img_crop_width, 0],
[img_crop_width, img_crop_height],
[0, img_crop_height]])
手動計算
得到長和框、裁剪四個座標
img_crop_width: 4, img_crop_height: 3
pts_std = [[0. 0.] [4. 0.][4. 3.][0. 3.]]
執行旋轉裁剪
# 獲取透視變換矩陣
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(points, pts_std)
# 進行透視變換
dst_img = cv2.warpPerspective(
img,
M, (img_crop_width, img_crop_height),
borderMode=cv2.BORDER_REPLICATE,
flags=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
# 獲取變換後圖像的高度和寬度
dst_img_height, dst_img_width = dst_img.shape[0:2]
# 如果高度和寬度的比例大於等於1.5,則旋轉圖像
if dst_img_height * 1.0 / dst_img_width >= 1.5:
dst_img = np.rot90(dst_img)獲取透視變換矩陣
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(points, pts_std)
- cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(points, pts_std) 計算並返回一個 3x3 的透視變換矩陣 M。
- points 是原始圖像中四個點的座標。
- pts_std 是目標圖像中對應四個點的座標。
-
透視變換矩陣 M 用於將原始圖像中的四個點映射到目標圖像中的四個點。
poinst = np.float32([[260, 100], [600, 100], [260, 400], [600, 400]]) pts_std = np.float32([[0, 0], [600, 0], [0, 600], [600, 600]])
進行透視變換
dst_img = cv2.warpPerspective(
img,
M, (img_crop_width, img_crop_height),
borderMode=cv2.BORDER_REPLICATE,
flags=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)- cv2.warpPerspective ,它會根據你提供的變換矩陣,把圖片中的某些部分拉伸、壓縮或扭曲到你希望的位置。
- img 是輸入的原始圖像。
- M 是透視變換矩陣。
- (img_crop_width, img_crop_height) 指定輸出圖像的大小。
- borderMode=cv2.BORDER_REPLICATE 當變換過程中有些像素點移到圖像邊界外時,使用邊緣的像素顏色填充這些位置。
示例完整代碼
# 進行切片和旋轉
def get_rotate_crop(img, points):
d = 0.0
# 使用高斯面積公式計算多邊形的有向面積
for index in range(-1, 3):
d += -0.5 * (points[index + 1][1] + points[index][1]) * (
points[index + 1][0] - points[index][0])
# 如果面積為負,交換點的位置以確保順時針順序
if d < 0:
tmp = np.array(points)
points[1], points[3] = tmp[3], tmp[1]
try:
# 計算裁剪圖像的寬度
img_crop_width = int(
max(
np.linalg.norm(points[0] - points[1]),
np.linalg.norm(points[2] - points[3])))
# 計算裁剪圖像的高度
img_crop_height = int(
max(
np.linalg.norm(points[0] - points[3]),
np.linalg.norm(points[1] - points[2])))
# 標註的目標座標
pts_std = np.float32([[0, 0], [img_crop_width, 0],
[img_crop_width, img_crop_height],
[0, img_crop_height]])
# 獲取透視變換矩陣
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(points, pts_std)
# 進行透視變換
dst_img = cv2.warpPerspective(
img,
M, (img_crop_width, img_crop_height),
borderMode=cv2.BORDER_REPLICATE,
flags=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
# 獲取變換後圖像的高度和寬度
dst_img_height, dst_img_width = dst_img.shape[0:2]
# 如果高度和寬度的比例大於等於1.5,則旋轉圖像
if dst_img_height * 1.0 / dst_img_width >= 1.5:
dst_img = np.rot90(dst_img)
return dst_img
except Exception as e:
print(e)參考文章
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shoelace_formula
https://waiterxiaoyy.github.io/2020/03/20/%E9%9E%8B%E5%B8%A6%...