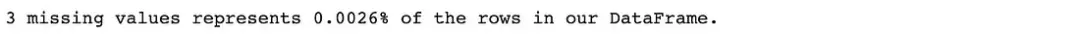數據清理是數據分析過程中的關鍵步驟,它涉及識別缺失值、重複行、異常值和不正確的數據類型。獲得乾淨可靠的數據對於準確的分析和建模非常重要。
本文將介紹以下6個經常使用的數據清理操作:
檢查缺失值、檢查重複行、處理離羣值、檢查所有列的數據類型、刪除不必要的列、數據不一致處理
第一步,讓我們導入庫和數據集。
# Import libraries
import pandas as pd
# Read data from a CSV file
df = pd.read_csv('filename.csv')檢查缺失值
isnull()方法可以用於查看數據框或列中的缺失值。
# Check for missing values in the dataframe
df.isnull()
# Check the number of missing values in the dataframe
df.isnull().sum().sort_values(ascending=False) # Check for missing values in the 'Customer Zipcode' column
df['Customer Zipcode'].isnull().sum()
# Check what percentage of the data frame these 3 missing values ••represent
print(f"3 missing values represents {(df['Customer Zipcode'].isnull().sum() / df.shape[0] * 100).round(4)}% of the rows in our DataFrame.")Zipcode列中有3個缺失值
dropna()可以刪除包含至少一個缺失值的任何行或列。
# Drop all the rows where at least one element is missing
df = df.dropna()
# or df.dropna(axis=0) **(axis=0 for rows and axis=1 for columns)
# Note: inplace=True modifies the DataFrame rather than creating a new one
df.dropna(inplace=True)
# Drop all the columns where at least one element is missing
df.dropna(axis=1, inplace=True)
# Drop rows with missing values in specific columns
df.dropna(subset = ['Additional Order items', 'Customer Zipcode'], inplace=True)fillna()也可以用更合適的值替換缺失的值,例如平均值、中位數或自定義值。
# Fill missing values in the dataset with a specific value
df = df.fillna(0)
# Replace missing values in the dataset with median
df = df.fillna(df.median())
# Replace missing values in Order Quantity column with the mean of Order Quantities
df['Order Quantity'].fillna(df["Order Quantity"].mean, inplace=True)檢查重複行
duplicate()方法可以查看重複的行。
# Check duplicate rows
df.duplicated()
# Check the number of duplicate rows
df.duplicated().sum()drop_duplates()可以使用這個方法刪除重複的行。
# Drop duplicate rows (but only keep the first row)
df = df.drop_duplicates(keep='first') #keep='first' / keep='last' / keep=False
# Note: inplace=True modifies the DataFrame rather than creating a new one
df.drop_duplicates(keep='first', inplace=True)處理離羣值
異常值是可以顯著影響分析的極端值。可以通過刪除它們或將它們轉換為更合適的值來處理它們。
describe()的maximum和mean之類的信息可以幫助我們查找離羣值。
# Get a statistics summary of the dataset
df["Product Price"].describe()max”值:1999。其他數值都不接近1999年,而平均值是146,所以可以確定1999是一個離羣值,需要處理
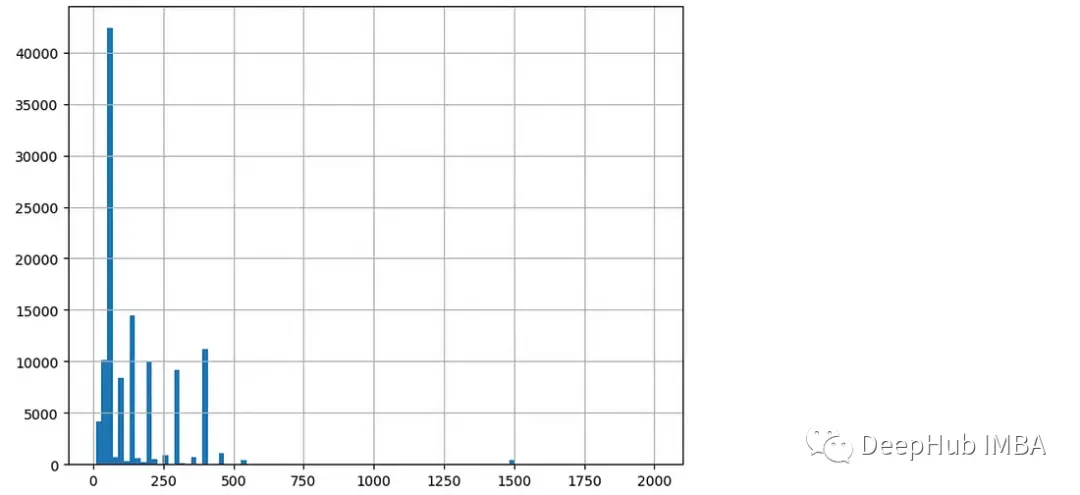
或者還可以繪製直方圖查看數據的分佈。
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
df["Product Price"].hist(bins=100)在直方圖中,可以看到大部分的價格數據都在0到500之間。
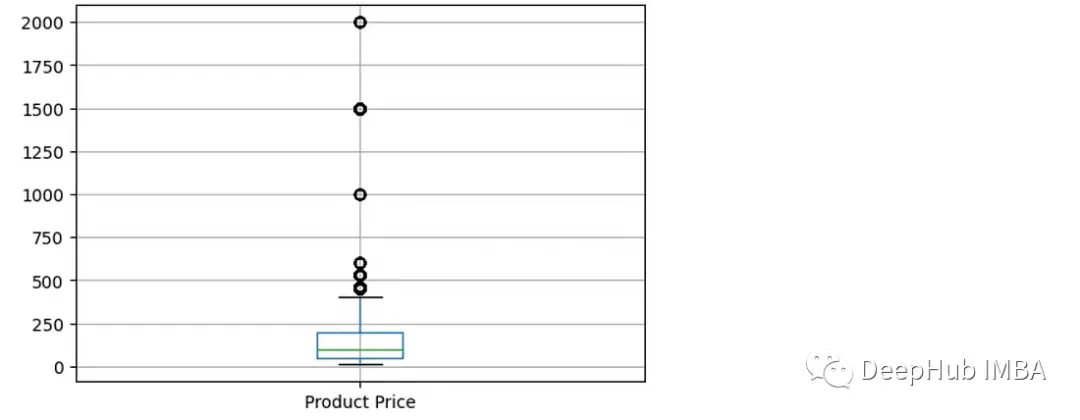
箱線圖在檢測異常值時也很有用。
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
df.boxplot(column=['Product Price'])可以看到價格列有多個離羣值數據點。(高於400的值)
檢查列的數據類型
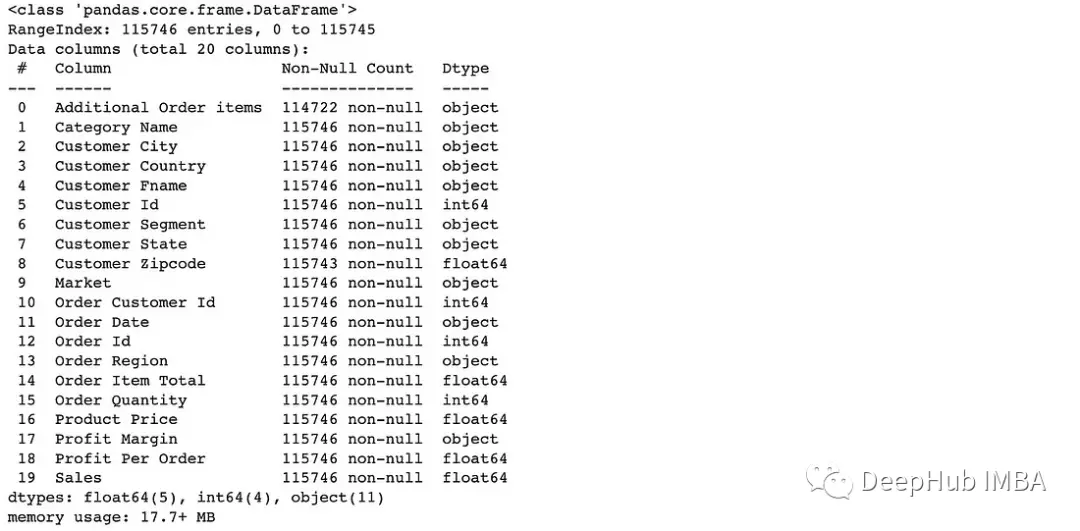
info()可以查看數據集中列的數據類型。
# Provide a summary of dataset
df.info()to_datetime()方法將列轉換為日期時間數據類型。
# Convert data type of Order Date column to date
df["Order Date"] = pd.to_datetime(df["Order Date"])to_numeric()可以將列轉換為數字數據類型(例如,整數或浮點數)。
# Convert data type of Order Quantity column to numeric data type
df["Order Quantity"] = pd.to_numeric(df["Order Quantity"])to_timedelta()方法將列轉換為timedelta數據類型,如果值表示持續時間,可以使用這個函數
# Convert data type of Duration column to timedelta type
df["Duration "] = pd.to_timedelta(df["Duration"])刪除不必要的列
drop()方法用於從數據框中刪除指定的行或列。
# Drop Order Region column
# (axis=0 for rows and axis=1 for columns)
df = df.drop('Order Region', axis=1)
# Drop Order Region column without having to reassign df (using inplace=True)
df.drop('Order Region', axis=1, inplace=True)
# Drop by column number instead of by column label
df = df.drop(df.columns[[0, 1, 3]], axis=1) # df.columns is zero-based數據不一致處理
數據不一致可能是由於格式或單位不同造成的。Pandas提供字符串方法來處理不一致的數據。
str.lower() & str.upper()這兩個函數用於將字符串中的所有字符轉換為小寫或大寫。它有助於標準化DataFrame列中字符串的情況。
# Rename column names to lowercase
df.columns = df.columns.str.lower() # Rename values in Customer Fname column to uppercase
df["Customer Fname"] = df["Customer Fname"].str.upper()str.strip()函數用於刪除字符串值開頭或結尾可能出現的任何額外空格。
# In Customer Segment column, convert names to lowercase and remove leading/trailing spaces
df['Customer Segment'] = df['Customer Segment'].str.lower().str.strip()replace()函數用於用新值替換DataFrame列中的特定值。
# Replace values in dataset
df = df.replace({"CA": "California", "TX": "Texas"}) # Replace values in a spesific column
df["Customer Country"] = df["Customer Country"].replace({"United States": "USA", "Puerto Rico": "PR"})mapping()可以創建一個字典,將不一致的值映射到標準化的對應值。然後將此字典與replace()函數一起使用以執行替換。
# Replace specific values using mapping
mapping = {'CA': 'California', 'TX': 'Texas'}
df['Customer State'] = df['Customer State'].replace(mapping)rename()函數用於重命名DataFrame的列或索引標籤。
# Rename some columns
df.rename(columns={'Customer City': 'Customer_City', 'Customer Fname' : 'Customer_Fname'}, inplace=True)
# Rename some columns
new_names = {'Customer Fname':'Customer_Firstname', 'Customer Fname':'Customer_Fname'}
df.rename(columns=new_names, inplace=True)
df.head()總結
Python pandas包含了豐富的函數和方法集來處理丟失的數據,刪除重複的數據,並有效地執行其他數據清理操作。
使用pandas功能,數據科學家和數據分析師可以簡化數據清理工作流程,並確保數據集的質量和完整性。
https://avoid.overfit.cn/post/d594591441dd47b2b1a6264c1c71368a
作者:Python Fundamentals