二叉搜索樹的侷限
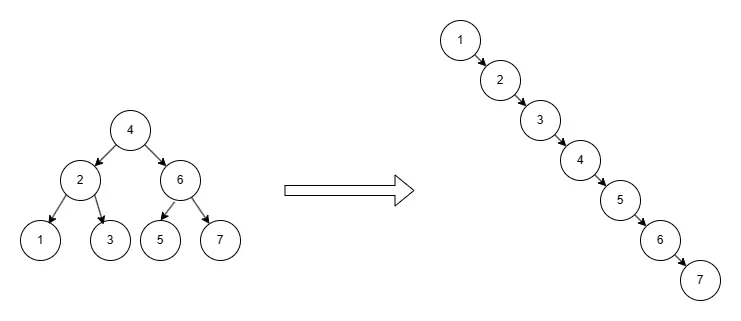
由於二叉樹的結構特性,將數據存儲到二叉搜索樹中,其時間複雜度可以從存儲在線性結構的的 O(N) 變成 O(log2 N) 。但這只是在理想的情況下的效率(如圖1 左),在實際的操作,樹的結構會不斷的變換,極端的情況下,可以變為線性結構,時間複雜度近乎於 O(N)。 在數據量非常大情況下,查詢速度會非常之低,這不是我們希望的結果。於是平衡樹的概念被提出來了。
圖1
什麼是平衡樹
平衡樹(Balanced Tree)是一種特殊的二叉搜索樹,它通過自動調整節點的插入和刪除操作,以保持樹的平衡性。在平衡樹中,任何節點的左右子樹的高度差不超過一個預定義的常數(自平衡)。
平衡樹的概念是由 G. M. Adelson-Velsky和Evgenii Landis 兩位計算機科學家提出來的,並提供了平衡樹的實現--AVL 樹, 該樹的名稱就是由兩位作者的姓氏命名的,他們在1962年的論文 An algorithm for the organization of information 中公開了這一數據結構。
當然,平衡樹不止有 AVL 樹一種,像後面出現的 2-3 樹, 2-3-4 樹, 紅黑樹等都是平衡樹的實現。
AVL 樹的特性
AVL樹具有以下特性:
- 每個節點都存儲一個關鍵字值。
- 對於任意節點,它的左子樹和右子樹都是AVL樹。
- 對於任意節點,其左子樹中的關鍵字值小於等於節點的關鍵字值,而其右子樹中的關鍵字值大於等於節點的關鍵字值。
- 每個節點都有一個平衡因子(Balance Factor),它表示其左子樹的高度減去右子樹的高度。平衡因子可以是 -1、0 或 1。
- 對於AVL樹中的每個節點,其平衡因子必須為 -1、0 或 1。如果一個節點的平衡因子不在這個範圍內,那麼它就不是AVL樹,需要進行平衡操作以恢復平衡性。
由第 3 點看出 AVL 是一棵二叉搜索樹,根據二叉搜索樹的特性,AVL 樹針對 4 種情況 提供了左旋和右旋的操作,以保證樹結構在插入和刪除操作後,始終保持自平衡(第 4、5 點)。
因此,在最壞的情況下, AVL 樹的查詢、插入、刪除操作的效率都為 O(log N)。
旋轉 --AVL 樹的核心操作
AVL 樹在查詢操作上與 一般二叉搜索樹沒有區別,而在插入和刪除操作後,由於樹的平衡性被打破,需要重新調整樹的結構,以保證自平衡。
通過旋轉調整平衡
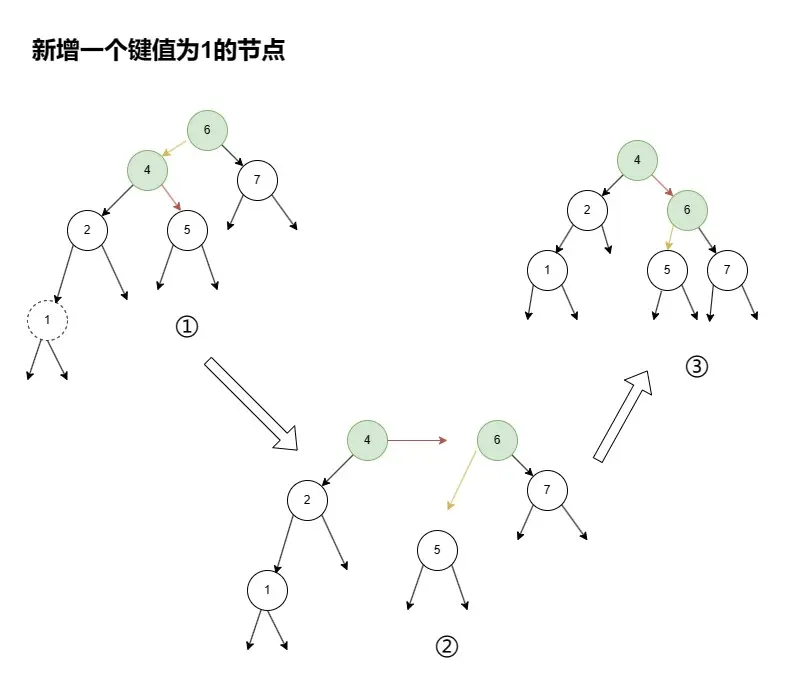
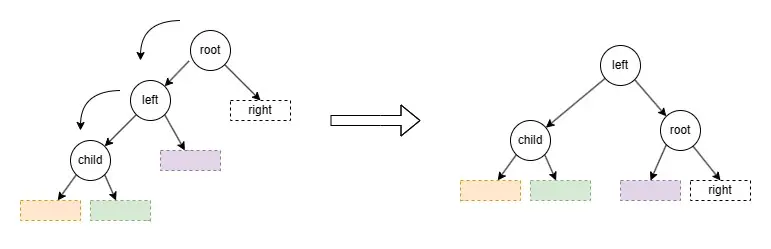
如圖2 所示,新增加一個鍵值為1的節點後, 節點6 的左子樹的高度1由原來的 2 變成了 3 ,而其右子樹的高度為 1。 左右子樹的高度差 大於了 1, 不再符合一個 AVL 樹的定義。 因此,需要在操作後,進行旋轉。
在這個例子中,需要進行向右旋轉,根節點由原來鍵值為6 的節點,變成了 鍵值為 4 的節點。
從 ① 到 ③ 的變換後,該樹依舊為一顆二叉搜索樹,這個性質非常的重要。
圖2
上面是 一個具體的例子,現在把旋轉操作抽象出來,在插入和刪除後,將會出現四種不平衡的類型。 我們分成四種情況進行討論,分別為 <u>左左</u>、<u>右右</u>、 <u>左右</u>、<u>右左</u>。
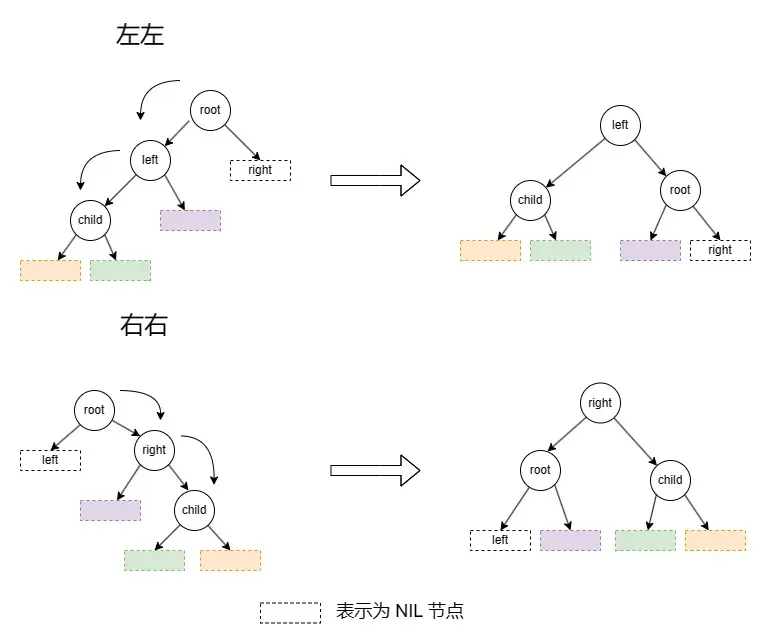
左左 和 右右
出現這兩種情況時(圖3),比較容易處理,只需要進行一次旋轉操作。
當增加、刪除操作後,計算左右子樹高度差,if(左子樹的高度 - 右子樹高度 > 1):
if (child < left) :
即為左左情況,需要進行右旋
當增加、刪除操作後,計算左右子樹高度差,if(左子樹的高度 - 右子樹高度 < -1):
if (child > right) :
即為右右情況,需要進行左旋圖3
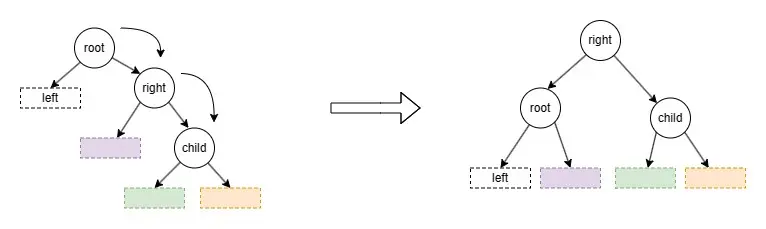
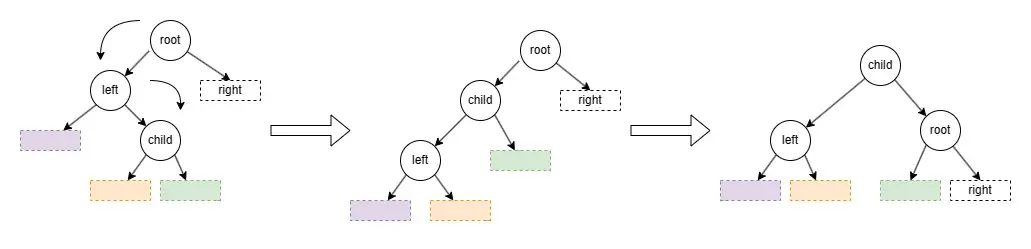
左右 和 左右
出現這兩種情況時(圖4),需要進行兩次旋轉操作。
當增加、刪除操作後,計算左右子樹高度差,if(左子樹的高度 - 右子樹高度 > 1):
if (child > left) :
即為左右情況:
① 對 left 子樹進行左旋操作
② 對 root 子樹進行右旋操作
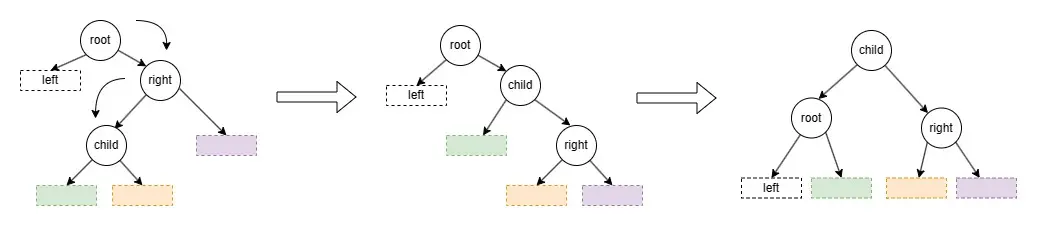
當增加、刪除操作後,計算左右子樹高度差,if(左子樹的高度 - 右子樹高度 < -1):
if (child < right) :
即為右左情況:
① 對 right 子樹進行右旋操作
② 對 root 子樹進行左旋操作 圖4
可以看出,上面四種情況使用到了兩種操作, 左旋和右旋,下面是左旋和右旋的實現。
左旋實現
## 下面是左旋的偽代碼實現
AVLNode leftRoute(AVLNode root) {
AVLNode newRoot = root.right; // right 節點作為最終返回的節點
AVLNode subTree = newRoot.left; // 臨時存儲如下圖的紫色部分,等下作為 root 的右子樹
root.right = subTree;
newRoot.left = root;
return newRoot; // 將調整好的樹重新返回
}右旋實現
## 下面是右旋的偽代碼實現
AVLNode rightRoute(AVLNode root) {
AVLNode newRoot = root.left; // left 節點作為最終返回的節點
AVLNode subTree = newRoot.right; // 臨時存儲如下圖的紫色部分,等下作為 root 的左子樹
root.left = subTree;
newRoot.right = root;
return newRoot; // 將調整好的樹重新返回
}可看到左旋和右旋操作的代碼量非常的簡單,而調整左右,和右左兩種情況,只需要兩次調用上面的方法即可。
左右情況的實現
## 下面是左右情況的偽代碼實現
AVLNode leftRight(AVLNode root) {
root.left = leftRoute(root.left);
return rightRoute(root);
}右左情況的實現
## 下面是左右情況的偽代碼實現
AVLNode rightLeft(AVLNode root) {
root.right = rightRoute(root.right);
return leftRoute(root);
}以上就是 AVL 樹的核心操作了,AVL 樹實現二叉搜索樹實現的區別就是,在增加和刪除和結束後,需要進行判斷高度差是否 > 1,如果 > 1 則需要根據上面四種情況進行旋轉操作。
構建一顆 AVL 樹
下面是 AVL 樹的 Java 實現,在這裏 key 為 int 類型,方便更專注與數據結構本身的學習。在實際的應用中,可根據需要將在節點中增加泛型,實現 Comparable 方法。
// AVLNode表示AVL樹的節點
class AVLNode {
int key; // 節點的關鍵字值
int height; // 節點的高度
AVLNode left; // 左子節點
AVLNode right; // 右子節點
public AVLNode(int key) {
this.key = key;
this.height = 1;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// AVLTree表示AVL樹
public class AVLTree {
AVLNode root; // 樹的根節點
// 獲取節點的高度
private int getHeight(AVLNode node) {
if (node == null)
return 0;
return node.height;
}
// 獲取節點的平衡因子
private int getBalanceFactor(AVLNode node) {
if (node == null)
return 0;
return getHeight(node.left) - getHeight(node.right);
}
// 更新節點的高度
private void updateHeight(AVLNode node) {
int leftHeight = getHeight(node.left);
int rightHeight = getHeight(node.right);
node.height = Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
// 執行左旋操作
private AVLNode leftRotate(AVLNode node) {
AVLNode newRoot = node.right;
AVLNode subtree = newRoot.left;
newRoot.left = node;
node.right = subtree;
updateHeight(node);
updateHeight(newRoot);
return newRoot;
}
// 執行右旋操作
private AVLNode rightRotate(AVLNode node) {
AVLNode newRoot = node.left;
AVLNode subtree = newRoot.right;
newRoot.right = node;
node.left = subtree;
updateHeight(node);
updateHeight(newRoot);
return newRoot;
}
// 插入節點到AVL樹中
public void insert(int key) {
root = insertNode(root, key);
}
private AVLNode insertNode(AVLNode node, int key) {
if (node == null)
return new AVLNode(key);
if (key < node.key) {
node.left = insertNode(node.left, key);
} else if (key > node.key) {
node.right = insertNode(node.right, key);
} else {
return node;
} // 忽略重複的關鍵字值
updateHeight(node);
int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(node);
// 左左情況,執行右旋
if (balanceFactor > 1 && key < node.left.key)
return rightRotate(node);
// 右右情況,執行左旋
if (balanceFactor < -1 && key > node.right.key)
return leftRotate(node);
// 左右情況,先對左子樹左旋,再對當前節點右旋
if (balanceFactor > 1 && key > node.left.key) {
node.left = leftRotate(node.left);
return rightRotate(node);
}
// 右左情況,先對右子樹右旋,再對當前節點左旋
if (balanceFactor < -1 && key < node.right.key) {
node.right = rightRotate(node.right);
return leftRotate(node);
}
return node;
}
// 刪除節點
public void delete(int key) {
root = deleteNode(root, key);
}
private AVLNode deleteNode(AVLNode node, int key) {
if (node == null)
return null;
if (key < node.key)
node.left = deleteNode(node.left, key);
else if (key > node.key)
node.right = deleteNode(node.right, key);
else {
// 找到要刪除的節點
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
// 葉節點,直接刪除
node = null;
} else if (node.left == null) {
// 只有右子樹,用右子樹替換當前節點
node = node.right;
} else if (node.right == null) {
// 只有左子樹,用左子樹替換當前節點
node = node.left;
} else {
// 左右子樹都存在,找到右子樹中的最小節點
AVLNode minNode = findMinNode(node.right);
node.key = minNode.key;
node.right = deleteNode(node.right, minNode.key);
}
}
if (node == null)
return null;
updateHeight(node);
int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(node);
// 左左情況,執行右旋
if (balanceFactor > 1 && getBalanceFactor(node.left) >= 0)
return rightRotate(node);
// 左右情況,先對左子樹左旋,再對當前節點右旋
if (balanceFactor > 1 && getBalanceFactor(node.left) < 0) {
node.left = leftRotate(node.left);
return rightRotate(node);
}
// 右右情況,執行左旋
if (balanceFactor < -1 && getBalanceFactor(node.right) <= 0)
return leftRotate(node);
// 右左情況,先對右子樹右旋,再對當前節點左旋
if (balanceFactor < -1 && getBalanceFactor(node.right) > 0) {
node.right = rightRotate(node.right);
return leftRotate(node);
}
return node;
}
// 查找樹中的最小節點
private AVLNode findMinNode(AVLNode node) {
AVLNode current = node;
while (current.left != null) {
current = current.left;
}
return current;
}
// 中序遍歷AVL樹
public void inorderTraversal() {
inorder(root);
}
private void inorder(AVLNode node) {
if (node != null) {
inorder(node.left);
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
inorder(node.right);
}
}
// 示例用法
public static void main(String[] args) {
AVLTree tree = new AVLTree();
tree.insert(10);
tree.insert(20);
tree.insert(30);
tree.insert(40);
tree.insert(50);
tree.insert(25);
System.out.println("AVL樹中序遍歷結果:");
tree.inorderTraversal();
tree.delete(30);
System.out.println("\n刪除節點30後的AVL樹中序遍歷結果:");
tree.inorderTraversal();
}
}
原文地址: https://daydream.icu/archives/AVL-tree
- 二叉樹的高度是指從根節點到最遠葉子節點的路徑上經過的節點數目。 ↩