Triton 是一種用於並行編程的語言和編譯器。它旨在提供一個基於 Python 的編程環境,以高效編寫自定義 DNN 計算內核,並能夠在現代 GPU 硬件上以最大吞吐量運行。
更多 Triton 中文文檔可訪問 →https://triton.hyper.ai/
在本教程中,您將編寫一個內存高效的 Dropout 實現,其狀態將由單個 int32 seed 組成。這與傳統 Dropout 實現不同,傳統實現通常由與輸入 shape 相同的位掩碼張量組成。
在這過程中,您將學習到以下內容:
- PyTorch 中 原生實現 Dropout 的侷限性。
- Triton 中的並行偽隨機數生成。
簡介
Dropout 是在 [SRIVASTAVA2014] 中引入的一種技術,用於改善低數據條件下深度神經網絡的性能,通常用於正則化。它接受一個向量作為輸入,並生成相同 shape 的輸出向量。輸出中的每個標量都有概率 p 被設為零,否則直接從輸入複製。這使得網絡在僅有輸入的 1−p 標量時也能表現良好。
在評估階段,為了充分利用網絡的能力,將 p 設為 0。但是簡單地將 p 設為 0 會增加輸出的範數,可能會人為地降低輸出的 softmax temperature。為了防止這種情況發生,輸出被縮放為 1/(1-p),這使得無論 dropout 概率如何都能保持一致的範數。
Baseline
首先看一下 baseline 的實現。
import tabulate
import torch
import triton
import triton.language as tl
@triton.jit
def _dropout(
x_ptr, # 輸入指針
x_keep_ptr, # pointer to a mask of 0s and 1s 由 0 和 1 組成的掩碼的指針
output_ptr, # pointer to the output 輸出指針
n_elements, # number of elements in the `x` tensor `x` 張量的元素數量
p, # probability that an element of `x` is changed to zero 元素 `x` 被設置為 0 的概率
BLOCK_SIZE: tl.constexpr,
):
pid = tl.program_id(axis=0)
block_start = pid * BLOCK_SIZE
offsets = block_start + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE)
mask = offsets < n_elements
# Load data
# 加載數據
x = tl.load(x_ptr + offsets, mask=mask)
x_keep = tl.load(x_keep_ptr + offsets, mask=mask)
# The line below is the crucial part, described in the paragraph above!
# 下一行是上段描述的關鍵部分
output = tl.where(x_keep, x / (1 - p), 0.0)
# Write-back output
# 寫回輸出
tl.store(output_ptr + offsets, output, mask=mask)
def dropout(x, x_keep, p):
output = torch.empty_like(x)
assert x.is_contiguous()
n_elements = x.numel()
grid = lambda meta: (triton.cdiv(n_elements, meta['BLOCK_SIZE']), )
_dropout[grid](x, x_keep, output, n_elements, p, BLOCK_SIZE=1024)
return output
# Input tensor
# 輸入張量
x = torch.randn(size=(10, )).cuda()
# Dropout mask
# Dropout 掩碼
p = 0.5
x_keep = (torch.rand(size=(10, )) > p).to(torch.int32).cuda()
#
output = dropout(x, x_keep=x_keep, p=p)
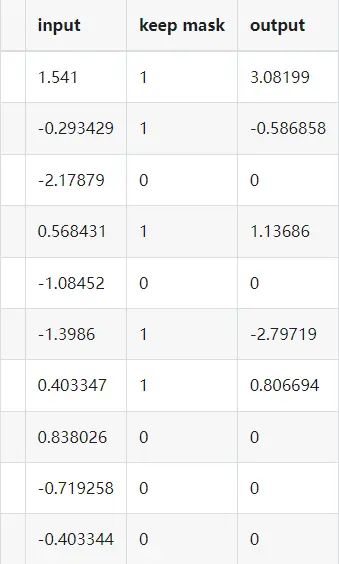
print(tabulate.tabulate([
["input"] + x.tolist(),
["keep mask"] + x_keep.tolist(),
["output"] + output.tolist(),
]))Out:
種子化 Dropout
上述 Dropout 實現效果良好,但管理 Dropout 狀態可能會變得複雜,特別是在考慮反向傳播和重新計算/檢查點場景時。在這裏,我們描述一種替代實現,它具有以下優點:
- 更小的內存佔用。
- 較少的數據移動。
- 簡化了在多次調用內核函數時持久化隨機性的管理。
生成 Triton 中的偽隨機數很簡單!在本教程中,我們將使用 triton.language.rand 函數,該函數基於給定的種子和一組 int32 偏移量生成一個塊的均勻分佈的 float32 值,範圍在 (0, 1) 內。但如果你需要,Triton 也提供其他隨機數生成策略。
注意 Triton 的 PRNG 實現基於 Philox 算法(詳見 [SALMON2011])。
現在將所有內容整合起來。
@triton.jit
def _seeded_dropout(
x_ptr,
output_ptr,
n_elements,
p,
seed,
BLOCK_SIZE: tl.constexpr,
):
# compute memory offsets of elements handled by this instance
# 計算由此實例處理的元素的內存偏移量
pid = tl.program_id(axis=0)
block_start = pid * BLOCK_SIZE
offsets = block_start + tl.arange(0, BLOCK_SIZE)
# load data from x
# 從 x 讀取數據
mask = offsets < n_elements
x = tl.load(x_ptr + offsets, mask=mask)
# randomly prune it
# 隨機修剪
random = tl.rand(seed, offsets)
x_keep = random > p
# write-back
# 寫回
output = tl.where(x_keep, x / (1 - p), 0.0)
tl.store(output_ptr + offsets, output, mask=mask)
def seeded_dropout(x, p, seed):
output = torch.empty_like(x)
assert x.is_contiguous()
n_elements = x.numel()
grid = lambda meta: (triton.cdiv(n_elements, meta['BLOCK_SIZE']), )
_seeded_dropout[grid](x, output, n_elements, p, seed, BLOCK_SIZE=1024)
return output
x = torch.randn(size=(10, )).cuda()
# Compare this to the baseline - dropout mask is never instantiated!
# 與基線相比 - dropout 掩碼從未被實例化!
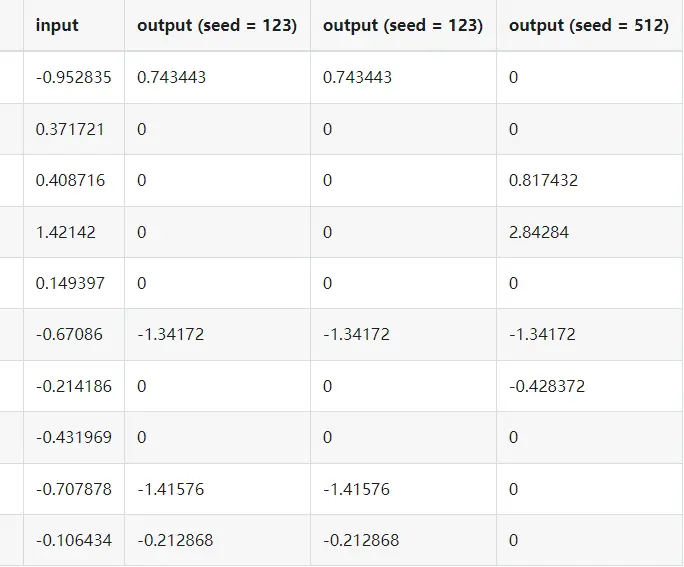
output = seeded_dropout(x, p=0.5, seed=123)
output2 = seeded_dropout(x, p=0.5, seed=123)
output3 = seeded_dropout(x, p=0.5, seed=512)
print(tabulate.tabulate([
["input"] + x.tolist(),
["output (seed = 123)"] + output.tolist(),
["output (seed = 123)"] + output2.tolist(),
["output (seed = 512)"] + output3.tolist(),
]))Out:
大功告成!我們現在有了一個 Triton 內核,可以在給定相同種子的情況下應用一致的 dropout 掩碼。與傳統的 dropout 實現相比,這種方法減少了內存開銷並簡化了狀態管理。
練習
- 擴展內核以處理矩陣,並使用一個種子向量 — 每行一個種子。
- 添加對 striding 的支持。
- (挑戰)實現稀疏 Johnson-Lindenstrauss 變換的內核,每次使用種子動態生成投影矩陣。
參考文獻
- [SALMON2011] John K. Salmon, Mark A. Moraes, Ron O. Dror, and David E. Shaw, "Parallel Random Numbers: As Easy as 1, 2, 3", 2011
- [SRIVASTAVA2014] Nitish Srivastava et al., "Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting", JMLR 2014
Download Jupyter notebook: 04-low-memory-dropout.ipynb
Download Python source code: 04-low-memory-dropout.py
Download zipped: 04-low-memory-dropout.zip