大家好,我是半夏之沫 😁😁 一名金融科技領域的JAVA系統研發😊😊
我希望將自己工作和學習中的經驗以最樸實,最嚴謹的方式分享給大家,共同進步👉💓👈
👉👉👉👉👉👉👉👉💓寫作不易,期待大家的關注和點贊💓👈👈👈👈👈👈👈👈
👉👉👉👉👉👉👉👉💓關注微信公眾號【技術探界】 💓👈👈👈👈👈👈👈👈
前言
本文將對Druid數據庫連接池的源碼進行分析和學習,以瞭解Druid數據庫連接池的工作原理。Druid數據庫連接池的基本邏輯幾乎全部在DruidDataSource類中,所以本文主要是圍繞DruidDataSource的各項功能展開論述。
Druid版本:1.2.11
正文
一. DruidDataSource初始化
DruidDataSource初始化有兩種方式,如下所示。
- 將
DruidDataSource實例創建出來後,主動調用其init()方法完成初始化; - 首次調用
DruidDataSource的getConnection()方法時,會調用到init()方法完成初始化。
由於init()方法過長,下面將分點介紹init()方法完成的關鍵事情。
1. 雙重檢查inited狀態
對inited狀態進行Double Check,防止DruidDataSource初始化兩次。源碼示意如下。
public void init() throws SQLException {
if (inited) {
return;
}
......
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
try {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new SQLException("interrupt", e);
}
boolean init = false;
try {
if (inited) {
return;
}
......
} catch (SQLException e) {
......
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
......
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
......
} catch (Error e) {
......
} finally {
inited = true;
lock.unlock();
......
}
}2. 判斷數據庫類型
根據jdbcUrl得到數據庫類型dbTypeName。源碼如下所示。
if (this.dbTypeName == null || this.dbTypeName.length() == 0) {
this.dbTypeName = JdbcUtils.getDbType(jdbcUrl, null);
}3. 參數校驗
對一些關鍵參數進行校驗。源碼如下所示。
// 連接池最大連接數量不能小於等於0
if (maxActive <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("illegal maxActive " + maxActive);
}
// 連接池最大連接數量不能小於最小連接數量
if (maxActive < minIdle) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("illegal maxActive " + maxActive);
}
// 連接池初始連接數量不能大於最大連接數量
if (getInitialSize() > maxActive) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("illegal initialSize " + this.initialSize + ", maxActive " + maxActive);
}
// 不允許同時開啓基於日誌手段記錄連接池狀態和全局狀態監控
if (timeBetweenLogStatsMillis > 0 && useGlobalDataSourceStat) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeBetweenLogStatsMillis not support useGlobalDataSourceStat=true");
}
// 連接最大空閒時間不能小於連接最小空閒時間
if (maxEvictableIdleTimeMillis < minEvictableIdleTimeMillis) {
throw new SQLException("maxEvictableIdleTimeMillis must be grater than minEvictableIdleTimeMillis");
}
// 不允許開啓了保活機制但保活間隔時間小於等於回收檢查時間間隔
if (keepAlive && keepAliveBetweenTimeMillis <= timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis) {
throw new SQLException("keepAliveBetweenTimeMillis must be grater than timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis");
}4. SPI機制加載過濾器
調用到DruidDataSource#initFromSPIServiceLoader方法,基於SPI機制加載過濾器Filter。源碼如下所示。
private void initFromSPIServiceLoader() {
if (loadSpifilterSkip) {
return;
}
if (autoFilters == null) {
List<Filter> filters = new ArrayList<Filter>();
// 基於ServiceLoader加載Filter
ServiceLoader<Filter> autoFilterLoader = ServiceLoader.load(Filter.class);
// 遍歷加載的每一個Filter,根據@AutoLoad註解的屬性判斷是否加載該Filter
for (Filter filter : autoFilterLoader) {
AutoLoad autoLoad = filter.getClass().getAnnotation(AutoLoad.class);
if (autoLoad != null && autoLoad.value()) {
filters.add(filter);
}
}
autoFilters = filters;
}
// 將每個需要加載的Filter添加到filters字段中,並去重
for (Filter filter : autoFilters) {
if (LOG.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOG.info("load filter from spi :" + filter.getClass().getName());
}
addFilter(filter);
}
}5. 加載驅動
調用DruidDataSource#resolveDriver方法,根據配置的驅動名稱加載數據庫驅動。源碼如下所示。
protected void resolveDriver() throws SQLException {
if (this.driver == null) {
// 若沒有配置驅動名則嘗試從jdbcUrl中獲取
if (this.driverClass == null || this.driverClass.isEmpty()) {
this.driverClass = JdbcUtils.getDriverClassName(this.jdbcUrl);
}
// Mock驅動相關
if (MockDriver.class.getName().equals(driverClass)) {
driver = MockDriver.instance;
} else if ("com.alibaba.druid.support.clickhouse.BalancedClickhouseDriver".equals(driverClass)) {
// ClickHouse相關
Properties info = new Properties();
info.put("user", username);
info.put("password", password);
info.putAll(connectProperties);
driver = new BalancedClickhouseDriver(jdbcUrl, info);
} else {
if (jdbcUrl == null && (driverClass == null || driverClass.length() == 0)) {
throw new SQLException("url not set");
}
// 加載驅動
driver = JdbcUtils.createDriver(driverClassLoader, driverClass);
}
} else {
if (this.driverClass == null) {
this.driverClass = driver.getClass().getName();
}
}
}6. 初始化連接有效性校驗器
調用DruidDataSource#initValidConnectionChecker方法,初始化ValidConnectionChecker,用於校驗某個連接是否可用。源碼如下所示。
private void initValidConnectionChecker() {
if (this.validConnectionChecker != null) {
return;
}
String realDriverClassName = driver.getClass().getName();
// 不同的數據庫初始化不同的ValidConnectionChecker
if (JdbcUtils.isMySqlDriver(realDriverClassName)) {
// MySQL數據庫還支持使用ping的方式來校驗連接活性,這比執行一條簡單查詢語句來判活更高效
// 由usePingMethod參數決定是否開啓
this.validConnectionChecker = new MySqlValidConnectionChecker(usePingMethod);
} else if (realDriverClassName.equals(JdbcConstants.ORACLE_DRIVER)
|| realDriverClassName.equals(JdbcConstants.ORACLE_DRIVER2)) {
this.validConnectionChecker = new OracleValidConnectionChecker();
} else if (realDriverClassName.equals(JdbcConstants.SQL_SERVER_DRIVER)
|| realDriverClassName.equals(JdbcConstants.SQL_SERVER_DRIVER_SQLJDBC4)
|| realDriverClassName.equals(JdbcConstants.SQL_SERVER_DRIVER_JTDS)) {
this.validConnectionChecker = new MSSQLValidConnectionChecker();
} else if (realDriverClassName.equals(JdbcConstants.POSTGRESQL_DRIVER)
|| realDriverClassName.equals(JdbcConstants.ENTERPRISEDB_DRIVER)
|| realDriverClassName.equals(JdbcConstants.POLARDB_DRIVER)) {
this.validConnectionChecker = new PGValidConnectionChecker();
} else if (realDriverClassName.equals(JdbcConstants.OCEANBASE_DRIVER)
|| (realDriverClassName.equals(JdbcConstants.OCEANBASE_DRIVER2))) {
DbType dbType = DbType.of(this.dbTypeName);
this.validConnectionChecker = new OceanBaseValidConnectionChecker(dbType);
}
}7. 初始化全局狀態統計器
如果useGlobalDataSourceStat設置為true,則初始化全局狀態統計器,用於統計和分析數據庫連接池的性能數據。源碼片段如下所示。
if (isUseGlobalDataSourceStat()) {
dataSourceStat = JdbcDataSourceStat.getGlobal();
if (dataSourceStat == null) {
dataSourceStat = new JdbcDataSourceStat("Global", "Global", this.dbTypeName);
JdbcDataSourceStat.setGlobal(dataSourceStat);
}
if (dataSourceStat.getDbType() == null) {
dataSourceStat.setDbType(this.dbTypeName);
}
} else {
dataSourceStat = new JdbcDataSourceStat(this.name, this.jdbcUrl, this.dbTypeName, this.connectProperties);
}8. 初始化連接池數組並預熱
創建三個連接池數組,分別是connections(用於存放能獲取的連接對象),evictConnections(用於存放需要丟棄的連接對象)和keepAliveConnections(用於存放需要保活的連接對象)。連接池的預熱有兩種,如果配置了asyncInit為true,且異步線程池不為空,則執行異步連接池預熱,反之執行同步連接池預熱。
// 用於存放能獲取的連接對象,真正意義上的連接池
// 已經被獲取的連接不在其中
connections = new DruidConnectionHolder[maxActive];
// 用於存放需要被關閉丟棄的連接
evictConnections = new DruidConnectionHolder[maxActive];
// 用於存放需要保活的連接
keepAliveConnections = new DruidConnectionHolder[maxActive];
SQLException connectError = null;
// 有線程池且異步初始化配置為true,則異步預熱
if (createScheduler != null && asyncInit) {
for (int i = 0; i < initialSize; ++i) {
submitCreateTask(true);
}
} else if (!asyncInit) {
// 同步預熱,預熱連接數由initialSize配置
while (poolingCount < initialSize) {
try {
PhysicalConnectionInfo pyConnectInfo = createPhysicalConnection();
// 對DruidDataSource和Connection做了一層封裝
DruidConnectionHolder holder = new DruidConnectionHolder(this, pyConnectInfo);
connections[poolingCount++] = holder;
} catch (SQLException ex) {
LOG.error("init datasource error, url: " + this.getUrl(), ex);
if (initExceptionThrow) {
connectError = ex;
break;
} else {
Thread.sleep(3000);
}
}
}
if (poolingCount > 0) {
poolingPeak = poolingCount;
poolingPeakTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}9. 創建日誌記錄線程並啓動
調用DruidDataSource#createAndLogThread方法創建通過打印日誌來記錄連接池狀態的線程。createAndLogThread()方法如下所示。
private void createAndLogThread() {
// timeBetweenLogStatsMillis小於等於0表示不開啓打印日誌記錄連接池狀態的功能
if (this.timeBetweenLogStatsMillis <= 0) {
return;
}
String threadName = "Druid-ConnectionPool-Log-" + System.identityHashCode(this);
// 創建線程
logStatsThread = new LogStatsThread(threadName);
// 啓動線程
logStatsThread.start();
this.resetStatEnable = false;
}createAndLogThread()方法會創建LogStatsThread並啓動,即會調用到LogStatsThread的run()方法。LogStatsThread線程的run()方法如下所示。
public void run() {
try {
for (; ; ) {
try {
// 每間隔timeBetweenLogStatsMillis就打印一次連接池狀態
logStats();
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.error("logStats error", e);
}
Thread.sleep(timeBetweenLogStatsMillis);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}上述run()方法中會每間隔timeBetweenLogStatsMillis的時間就調用一次logStats()方法來打印連接池狀態。logStats()方法如下所示。
public void logStats() {
final DruidDataSourceStatLogger statLogger = this.statLogger;
if (statLogger == null) {
return;
}
// 拿到各種連接池的狀態
DruidDataSourceStatValue statValue = getStatValueAndReset();
// 打印
statLogger.log(statValue);
}在logStats()方法中會先調用getStatValueAndReset()方法來拿到各種連接池的狀態,然後調用DruidDataSourceStatLogger完成打印。最後看一眼getStatValueAndReset()方法裏面拿哪些連接池狀態,getStatValueAndReset()方法代碼片段如下所示。
public DruidDataSourceStatValue getStatValueAndReset() {
DruidDataSourceStatValue value = new DruidDataSourceStatValue();
lock.lock();
try {
value.setPoolingCount(this.poolingCount);
value.setPoolingPeak(this.poolingPeak);
value.setPoolingPeakTime(this.poolingPeakTime);
value.setActiveCount(this.activeCount);
value.setActivePeak(this.activePeak);
value.setActivePeakTime(this.activePeakTime);
value.setConnectCount(this.connectCount);
value.setCloseCount(this.closeCount);
value.setWaitThreadCount(lock.getWaitQueueLength(notEmpty));
value.setNotEmptyWaitCount(this.notEmptyWaitCount);
value.setNotEmptyWaitNanos(this.notEmptyWaitNanos);
value.setKeepAliveCheckCount(this.keepAliveCheckCount);
// 重置參數
this.poolingPeak = 0;
this.poolingPeakTime = 0;
this.activePeak = 0;
this.activePeakTime = 0;
this.connectCount = 0;
this.closeCount = 0;
this.keepAliveCheckCount = 0;
this.notEmptyWaitCount = 0;
this.notEmptyWaitNanos = 0;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
value.setName(this.getName());
value.setDbType(this.dbTypeName);
value.setDriverClassName(this.getDriverClassName());
......
value.setSqlSkipCount(this.getDataSourceStat().getSkipSqlCountAndReset());
value.setSqlList(this.getDataSourceStat().getSqlStatMapAndReset());
return value;
}10. 創建創建連接的線程並啓動
調用DruidDataSource#createAndStartCreatorThread方法來創建創建連接的線程CreateConnectionThread並啓動。createAndStartCreatorThread()方法如下所示。
protected void createAndStartCreatorThread() {
// 只有異步創建連接的線程池為空時,才創建CreateConnectionThread
if (createScheduler == null) {
String threadName = "Druid-ConnectionPool-Create-" + System.identityHashCode(this);
createConnectionThread = new CreateConnectionThread(threadName);
// 啓動線程
createConnectionThread.start();
return;
}
initedLatch.countDown();
}CreateConnectionThread只有在異步創建連接的線程池createScheduler為空時,才會被創建出來,並且在CreateConnectionThread的run()方法一開始,就會調用initedLatch的countDown()方法,其中initedLatch是一個初始值為2的CountDownLatch對象,另外一次countDown()調用在DestroyConnectionThread的run()方法中,目的就是init()方法執行完以前,創建連接的線程和銷燬連接的線程一定要創建出來並啓動完畢。
createAndLogThread();
// 在內部會調用到initedLatch.countDown()
createAndStartCreatorThread();
// 在內部最終會調用initedLatch.countDown()
createAndStartDestroyThread();
initedLatch.await();11. 創建銷燬連接的線程並啓動
調用DruidDataSource#createAndStartDestroyThread方法來創建銷燬連接的線程DestroyConnectionThread並啓動。createAndStartDestroyThread()方法如下所示。
protected void createAndStartDestroyThread() {
// 銷燬連接的任務
destroyTask = new DestroyTask();
// 如果銷燬連接的線程池不會為空,則讓其週期執行銷燬連接的任務
if (destroyScheduler != null) {
long period = timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis;
if (period <= 0) {
period = 1000;
}
destroySchedulerFuture = destroyScheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(destroyTask, period, period,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
initedLatch.countDown();
return;
}
// 如果銷燬連接的線程池為空,則創建銷燬連接的線程
String threadName = "Druid-ConnectionPool-Destroy-" + System.identityHashCode(this);
destroyConnectionThread = new DestroyConnectionThread(threadName);
// 啓動線程
destroyConnectionThread.start();
}createAndStartDestroyThread()方法中會先判斷銷燬連接的線程池是否存在,如果存在,則不再創建DestroyConnectionThread,而是會讓銷燬連接的線程池來執行銷燬任務,如果不存在,則創建DestroyConnectionThread並啓動,此時initedLatch的countDown()調用是在DestroyConnectionThread的run()方法中。DestroyConnectionThread#run方法源碼如下所示。
public void run() {
// run()方法只要執行了,就調用initedLatch#countDown
initedLatch.countDown();
for (; ; ) {
// 每間隔timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis執行一次DestroyTask的run()方法
try {
if (closed || closing) {
break;
}
if (timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis > 0) {
Thread.sleep(timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis);
} else {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
break;
}
// 執行DestroyTask的run()方法來銷燬需要銷燬的線程
destroyTask.run();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
}
}DestroyConnectionThread#run方法只要被調用到,那麼就會調用initedLatch的countDown()方法,此時阻塞在init()方法中的initedLatch.await()方法上的線程就會被喚醒並繼續往下執行。
二. DruidDataSource連接創建
DruidDataSource連接的創建由CreateConnectionThread線程完成,其run()方法如下所示。
public void run() {
initedLatch.countDown();
long lastDiscardCount = 0;
int errorCount = 0;
for (; ; ) {
try {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
} catch (InterruptedException e2) {
break;
}
long discardCount = DruidDataSource.this.discardCount;
boolean discardChanged = discardCount - lastDiscardCount > 0;
lastDiscardCount = discardCount;
try {
// emptyWait為true表示生產連接線程需要等待,無需生產連接
boolean emptyWait = true;
// 發生了創建錯誤,且池中已無連接,且丟棄連接的統計沒有改變
// 此時生產連接線程需要生產連接
if (createError != null
&& poolingCount == 0
&& !discardChanged) {
emptyWait = false;
}
if (emptyWait
&& asyncInit && createCount < initialSize) {
emptyWait = false;
}
if (emptyWait) {
// 池中已有連接數大於等於正在等待連接的應用線程數
// 且當前是非keepAlive場景
// 且當前是非連續失敗
// 此時生產連接的線程在empty上等待
// keepAlive && activeCount + poolingCount < minIdle時會在shrink()方法中觸發emptySingal()來添加連接
// isFailContinuous()返回true表示連續失敗,即多次(默認2次)創建物理連接失敗
if (poolingCount >= notEmptyWaitThreadCount
&& (!(keepAlive && activeCount + poolingCount < minIdle))
&& !isFailContinuous()
) {
empty.await();
}
// 防止創建超過maxActive數量的連接
if (activeCount + poolingCount >= maxActive) {
empty.await();
continue;
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
......
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
PhysicalConnectionInfo connection = null;
try {
connection = createPhysicalConnection();
} catch (SQLException e) {
LOG.error("create connection SQLException, url: " + jdbcUrl + ", errorCode " + e.getErrorCode()
+ ", state " + e.getSQLState(), e);
errorCount++;
if (errorCount > connectionErrorRetryAttempts && timeBetweenConnectErrorMillis > 0) {
// 多次創建失敗
setFailContinuous(true);
// 如果配置了快速失敗,就喚醒所有在notEmpty上等待的應用線程
if (failFast) {
lock.lock();
try {
notEmpty.signalAll();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
if (breakAfterAcquireFailure) {
break;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(timeBetweenConnectErrorMillis);
} catch (InterruptedException interruptEx) {
break;
}
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
LOG.error("create connection RuntimeException", e);
setFailContinuous(true);
continue;
} catch (Error e) {
LOG.error("create connection Error", e);
setFailContinuous(true);
break;
}
if (connection == null) {
continue;
}
// 把連接添加到連接池
boolean result = put(connection);
if (!result) {
JdbcUtils.close(connection.getPhysicalConnection());
LOG.info("put physical connection to pool failed.");
}
errorCount = 0;
if (closing || closed) {
break;
}
}
}CreateConnectionThread的run()方法整體就是在一個死循環中不斷的等待,被喚醒,然後創建線程。當一個物理連接被創建出來後,會調用DruidDataSource#put方法將其放到連接池connections中,put()方法源碼如下所示。
protected boolean put(PhysicalConnectionInfo physicalConnectionInfo) {
DruidConnectionHolder holder = null;
try {
holder = new DruidConnectionHolder(DruidDataSource.this, physicalConnectionInfo);
} catch (SQLException ex) {
......
return false;
}
return put(holder, physicalConnectionInfo.createTaskId, false);
}
private boolean put(DruidConnectionHolder holder, long createTaskId, boolean checkExists) {
// 涉及到連接池中連接數量改變的操作,都需要加鎖
lock.lock();
try {
if (this.closing || this.closed) {
return false;
}
// 池中已有連接數已經大於等於最大連接數,則不再把連接加到連接池並直接返回false
if (poolingCount >= maxActive) {
if (createScheduler != null) {
clearCreateTask(createTaskId);
}
return false;
}
// 檢查重複添加
if (checkExists) {
for (int i = 0; i < poolingCount; i++) {
if (connections[i] == holder) {
return false;
}
}
}
// 連接放入連接池
connections[poolingCount] = holder;
// poolingCount++
incrementPoolingCount();
if (poolingCount > poolingPeak) {
poolingPeak = poolingCount;
poolingPeakTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
// 喚醒在notEmpty上等待連接的應用線程
notEmpty.signal();
notEmptySignalCount++;
if (createScheduler != null) {
clearCreateTask(createTaskId);
if (poolingCount + createTaskCount < notEmptyWaitThreadCount
&& activeCount + poolingCount + createTaskCount < maxActive) {
emptySignal();
}
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return true;
}put()方法會先將物理連接從PhysicalConnectionInfo中獲取出來並封裝成一個DruidConnectionHolder,DruidConnectionHolder就是Druid連接池中的連接。新添加的連接會存放在連接池數組connections的poolingCount位置,然後poolingCount會加1,也就是poolingCount代表着連接池中可以獲取的連接的數量。
三. DruidDataSource連接銷燬
DruidDataSource連接的創建由DestroyConnectionThread線程完成,其run()方法如下所示。
public void run() {
// run()方法只要執行了,就調用initedLatch#countDown
initedLatch.countDown();
for (; ; ) {
// 每間隔timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis執行一次DestroyTask的run()方法
try {
if (closed || closing) {
break;
}
if (timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis > 0) {
Thread.sleep(timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis);
} else {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
break;
}
// 執行DestroyTask的run()方法來銷燬需要銷燬的連接
destroyTask.run();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
}
}DestroyConnectionThread的run()方法就是在一個死循環中每間隔timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis的時間就執行一次DestroyTask的run()方法。DestroyTask#run方法實現如下所示。
public void run() {
// 根據一系列條件判斷並銷燬連接
shrink(true, keepAlive);
// RemoveAbandoned機制
if (isRemoveAbandoned()) {
removeAbandoned();
}
}在DestroyTask#run方法中會調用DruidDataSource#shrink方法來根據設定的條件來判斷出需要銷燬和保活的連接。DruidDataSource#shrink方法如下所示。
// checkTime參數表示在將一個連接進行銷燬前,是否需要判斷一下空閒時間
public void shrink(boolean checkTime, boolean keepAlive) {
// 加鎖
try {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
return;
}
// needFill = keepAlive && poolingCount + activeCount < minIdle
// needFill為true時,會調用empty.signal()喚醒生產連接的線程來生產連接
boolean needFill = false;
// evictCount記錄需要銷燬的連接數
// keepAliveCount記錄需要保活的連接數
int evictCount = 0;
int keepAliveCount = 0;
int fatalErrorIncrement = fatalErrorCount - fatalErrorCountLastShrink;
fatalErrorCountLastShrink = fatalErrorCount;
try {
if (!inited) {
return;
}
// checkCount = 池中已有連接數 - 最小空閒連接數
// 正常情況下,最多能夠將前checkCount個連接進行銷燬
final int checkCount = poolingCount - minIdle;
final long currentTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 正常情況下,需要遍歷池中所有連接
// 從前往後遍歷,i為數組索引
for (int i = 0; i < poolingCount; ++i) {
DruidConnectionHolder connection = connections[i];
// 如果發生了致命錯誤(onFatalError == true)且致命錯誤發生時間(lastFatalErrorTimeMillis)在連接建立時間之後
// 把連接加入到保活連接數組中
if ((onFatalError || fatalErrorIncrement > 0) && (lastFatalErrorTimeMillis > connection.connectTimeMillis)) {
keepAliveConnections[keepAliveCount++] = connection;
continue;
}
if (checkTime) {
// phyTimeoutMillis表示連接的物理存活超時時間,默認值是-1
if (phyTimeoutMillis > 0) {
// phyConnectTimeMillis表示連接的物理存活時間
long phyConnectTimeMillis = currentTimeMillis - connection.connectTimeMillis;
// 連接的物理存活時間大於phyTimeoutMillis,則將這個連接放入evictConnections數組
if (phyConnectTimeMillis > phyTimeoutMillis) {
evictConnections[evictCount++] = connection;
continue;
}
}
// idleMillis表示連接的空閒時間
long idleMillis = currentTimeMillis - connection.lastActiveTimeMillis;
// minEvictableIdleTimeMillis表示連接允許的最小空閒時間,默認是30分鐘
// keepAliveBetweenTimeMillis表示保活間隔時間,默認是2分鐘
// 如果連接的空閒時間小於minEvictableIdleTimeMillis且還小於keepAliveBetweenTimeMillis
// 則connections數組中當前連接之後的連接都會滿足空閒時間小於minEvictableIdleTimeMillis且還小於keepAliveBetweenTimeMillis
// 此時跳出遍歷,不再檢查其餘的連接
if (idleMillis < minEvictableIdleTimeMillis
&& idleMillis < keepAliveBetweenTimeMillis
) {
break;
}
// 連接的空閒時間大於等於允許的最小空閒時間
if (idleMillis >= minEvictableIdleTimeMillis) {
if (checkTime && i < checkCount) {
// i < checkCount這個條件的理解如下:
// 每次shrink()方法執行時,connections數組中只有索引0到checkCount-1的連接才允許被銷燬
// 這樣才能保證銷燬完連接後,connections數組中至少還有minIdle個連接
evictConnections[evictCount++] = connection;
continue;
} else if (idleMillis > maxEvictableIdleTimeMillis) {
// 如果空閒時間過久,已經大於了允許的最大空閒時間(默認7小時)
// 那麼無論如何都要銷燬這個連接
evictConnections[evictCount++] = connection;
continue;
}
}
// 如果開啓了保活機制,且連接空閒時間大於等於了保活間隔時間
// 此時將連接加入到保活連接數組中
if (keepAlive && idleMillis >= keepAliveBetweenTimeMillis) {
keepAliveConnections[keepAliveCount++] = connection;
}
} else {
// checkTime為false,那麼前checkCount個連接直接進行銷燬,不再判斷這些連接的空閒時間是否超過閾值
if (i < checkCount) {
evictConnections[evictCount++] = connection;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
// removeCount = 銷燬連接數 + 保活連接數
// removeCount表示本次從connections數組中拿掉的連接數
// 注:一定是從前往後拿,正常情況下最後minIdle個連接是安全的
int removeCount = evictCount + keepAliveCount;
if (removeCount > 0) {
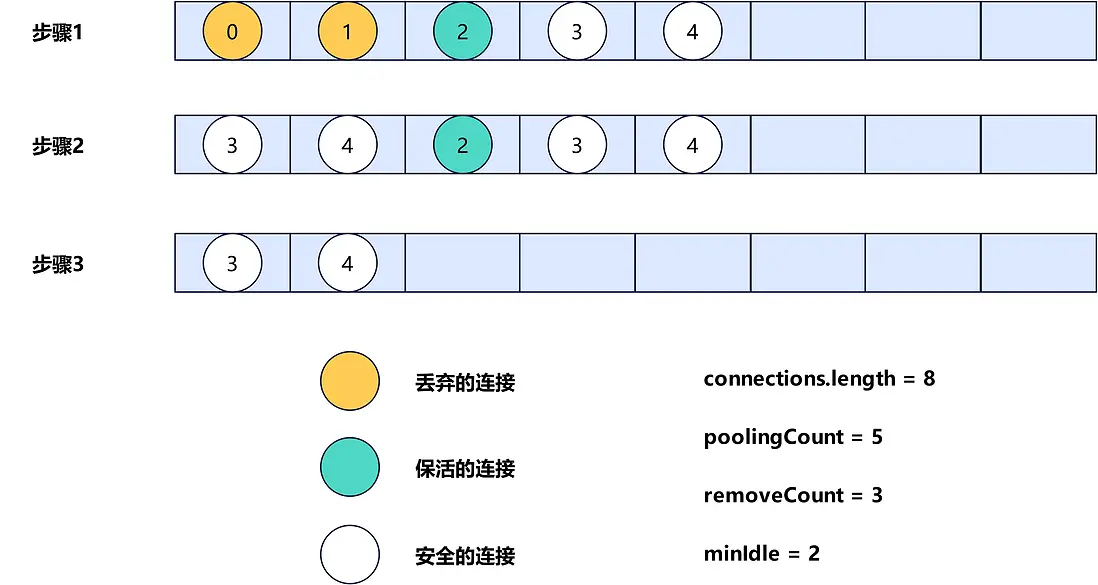
// [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, null, null, null] -> [3, 4, 2, 3, 4, null, null, null]
System.arraycopy(connections, removeCount, connections, 0, poolingCount - removeCount);
// [3, 4, 2, 3, 4, null, null, null] -> [3, 4, null, null, null, null, null, null, null]
Arrays.fill(connections, poolingCount - removeCount, poolingCount, null);
// 更新池中連接數
poolingCount -= removeCount;
}
keepAliveCheckCount += keepAliveCount;
// 如果池中連接數加上活躍連接數(借出去的連接)小於最小空閒連接數
// 則將needFill設為true,後續需要喚醒生產連接的線程來生產連接
if (keepAlive && poolingCount + activeCount < minIdle) {
needFill = true;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
if (evictCount > 0) {
// 遍歷evictConnections數組,銷燬其中的連接
for (int i = 0; i < evictCount; ++i) {
DruidConnectionHolder item = evictConnections[i];
Connection connection = item.getConnection();
JdbcUtils.close(connection);
destroyCountUpdater.incrementAndGet(this);
}
Arrays.fill(evictConnections, null);
}
if (keepAliveCount > 0) {
// 遍歷keepAliveConnections數組,對其中的連接做可用性校驗
// 校驗通過連接就放入connections數組,沒通過連接就銷燬
for (int i = keepAliveCount - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
DruidConnectionHolder holer = keepAliveConnections[i];
Connection connection = holer.getConnection();
holer.incrementKeepAliveCheckCount();
boolean validate = false;
try {
this.validateConnection(connection);
validate = true;
} catch (Throwable error) {
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("keepAliveErr", error);
}
}
boolean discard = !validate;
if (validate) {
holer.lastKeepTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
boolean putOk = put(holer, 0L, true);
if (!putOk) {
discard = true;
}
}
if (discard) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
lock.lock();
try {
discardCount++;
if (activeCount + poolingCount <= minIdle) {
emptySignal();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
this.getDataSourceStat().addKeepAliveCheckCount(keepAliveCount);
Arrays.fill(keepAliveConnections, null);
}
// 如果needFill為true則喚醒生產連接的線程來生產連接
if (needFill) {
lock.lock();
try {
// 計算需要生產連接的個數
int fillCount = minIdle - (activeCount + poolingCount + createTaskCount);
for (int i = 0; i < fillCount; ++i) {
emptySignal();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} else if (onFatalError || fatalErrorIncrement > 0) {
lock.lock();
try {
emptySignal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}在DruidDataSource#shrink方法中,核心邏輯是遍歷connections數組中的連接,並判斷這些連接是需要銷燬還是需要保活。通常情況下,connections數組中的前checkCount(checkCount = poolingCount - minIdle)個連接是“危險”的,因為這些連接只要滿足了:空閒時間 >= minEvictableIdleTimeMillis(允許的最小空閒時間),那麼就需要被銷燬,而connections數組中的最後minIdle個連接是“相對安全”的,因為這些連接只有在滿足:空閒時間 > maxEvictableIdleTimeMillis(允許的最大空閒時間)時,才會被銷燬。這麼判斷的原因,主要就是需要讓連接池裏能夠保證至少有minIdle個空閒連接可以讓應用線程獲取。
當確定好了需要銷燬和需要保活的連接後,此時會先將connections數組清理,只保留安全的連接,這個過程示意圖如下。
最後,會遍歷evictConnections數組,銷燬數組中的連接,遍歷keepAliveConnections數組,對其中的每個連接做可用性校驗,如果校驗可用,那麼就重新放回connections數組,否則銷燬。
四. DruidDataSource連接獲取
DruidDataSource獲取連接的入口方法是DruidDataSource#getConnection方法,實現如下。
public DruidPooledConnection getConnection() throws SQLException {
// maxWait表示獲取連接時最大等待時間,單位毫秒,默認值為-1
return getConnection(maxWait);
}
public DruidPooledConnection getConnection(long maxWaitMillis) throws SQLException {
// 首次獲取連接時觸發數據庫連接池初始化
init();
if (filters.size() > 0) {
FilterChainImpl filterChain = new FilterChainImpl(this);
return filterChain.dataSource_connect(this, maxWaitMillis);
} else {
// 直接獲取連接
return getConnectionDirect(maxWaitMillis);
}
}DruidDataSource#getConnection方法會調用到DruidDataSource#getConnectionDirect方法來獲取連接,實現如下所示。
public DruidPooledConnection getConnectionDirect(long maxWaitMillis) throws SQLException {
int notFullTimeoutRetryCnt = 0;
for (; ; ) {
DruidPooledConnection poolableConnection;
try {
// 從連接池拿到連接
poolableConnection = getConnectionInternal(maxWaitMillis);
} catch (GetConnectionTimeoutException ex) {
// 拿連接時有異常,可以重試
// 重試次數由notFullTimeoutRetryCount指定
if (notFullTimeoutRetryCnt <= this.notFullTimeoutRetryCount && !isFull()) {
notFullTimeoutRetryCnt++;
if (LOG.isWarnEnabled()) {
LOG.warn("get connection timeout retry : " + notFullTimeoutRetryCnt);
}
continue;
}
throw ex;
}
// 如果配置了testOnBorrow = true,那麼每次拿到連接後,都需要校驗這個連接的有效性
if (testOnBorrow) {
boolean validate = testConnectionInternal(poolableConnection.holder, poolableConnection.conn);
// 如果連接不可用,則銷燬連接,然後重新從池中獲取
if (!validate) {
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("skip not validate connection.");
}
discardConnection(poolableConnection.holder);
continue;
}
} else {
if (poolableConnection.conn.isClosed()) {
discardConnection(poolableConnection.holder);
continue;
}
// 如果配置testOnBorrow = fasle但testWhileIdle = true
// 則判斷連接空閒時間是否大於等於timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis
// 如果是,則校驗連接的有效性
if (testWhileIdle) {
final DruidConnectionHolder holder = poolableConnection.holder;
long currentTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
// lastActiveTimeMillis是連接最近一次活躍時間
// 新建連接,歸還連接到連接池,都會更新這個時間
long lastActiveTimeMillis = holder.lastActiveTimeMillis;
// lastExecTimeMillis是連接最近一次執行時間
// 新建連接,設置連接的事務是否自動提交,記錄SQL到事務信息中,都會更新這個時間
long lastExecTimeMillis = holder.lastExecTimeMillis;
// lastKeepTimeMillis是連接最近一次保活時間
// 在連接被保活並放回連接池時,會更新這個時間
long lastKeepTimeMillis = holder.lastKeepTimeMillis;
// 如果配置checkExecuteTime為true,則最近活躍時間取值為最近執行時間
if (checkExecuteTime
&& lastExecTimeMillis != lastActiveTimeMillis) {
lastActiveTimeMillis = lastExecTimeMillis;
}
// 如果連接最近一次做的操作是保活,那麼最近活躍時間取值為最近保活時間
if (lastKeepTimeMillis > lastActiveTimeMillis) {
lastActiveTimeMillis = lastKeepTimeMillis;
}
// 計算空閒時間
long idleMillis = currentTimeMillis - lastActiveTimeMillis;
// testWhileIdle為true時的判斷時間間隔
long timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis = this.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis;
if (timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis <= 0) {
// timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis如果小於等於0,那麼重置為60秒
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis = DEFAULT_TIME_BETWEEN_EVICTION_RUNS_MILLIS;
}
// 如果空閒時間大於等於timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis,則執行連接的有效性校驗
if (idleMillis >= timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis
|| idleMillis < 0
) {
boolean validate = testConnectionInternal(poolableConnection.holder, poolableConnection.conn);
if (!validate) {
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("skip not validate connection.");
}
discardConnection(poolableConnection.holder);
continue;
}
}
}
}
// 如果設置removeAbandoned為true
// 則將連接放到activeConnections活躍連接map中
if (removeAbandoned) {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace();
poolableConnection.connectStackTrace = stackTrace;
poolableConnection.setConnectedTimeNano();
poolableConnection.traceEnable = true;
activeConnectionLock.lock();
try {
activeConnections.put(poolableConnection, PRESENT);
} finally {
activeConnectionLock.unlock();
}
}
if (!this.defaultAutoCommit) {
poolableConnection.setAutoCommit(false);
}
return poolableConnection;
}
}DruidDataSource#getConnectionDirect方法中會先調用getConnectionInternal()方法從連接池中拿連接,然後如果開啓了testOnBorrow,則校驗一下連接的有效性,如果無效則重新調用getConnectionInternal()方法拿連接,直到拿到的連接通過校驗。如果沒有開啓testOnBorrow但是開啓了testWhileIdle,則會判斷連接的空閒時間是否大於等於timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis參數,如果滿足則校驗一下連接的有效性,若沒有通過校驗,那麼需要重新調用getConnectionInternal()方法拿連接,直到拿到的連接通過校驗或者連接的空閒時間小於timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis。
下面看一下實際從連接池拿連接的getConnectionInternal()方法的實現,如下所示。
private DruidPooledConnection getConnectionInternal(long maxWait) throws SQLException {
......
final long nanos = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(maxWait);
final int maxWaitThreadCount = this.maxWaitThreadCount;
DruidConnectionHolder holder;
// 在死循環中從連接池拿連接
// 一開始createDirect為false,表示先從池子中拿
for (boolean createDirect = false; ; ) {
if (createDirect) {
// createDirect為true表示直接創建連接
createStartNanosUpdater.set(this, System.nanoTime());
// creatingCount為0表示當前沒有其它連接正在被創建
if (creatingCountUpdater.compareAndSet(this, 0, 1)) {
// 創建物理連接
PhysicalConnectionInfo pyConnInfo = DruidDataSource.this.createPhysicalConnection();
holder = new DruidConnectionHolder(this, pyConnInfo);
holder.lastActiveTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
creatingCountUpdater.decrementAndGet(this);
directCreateCountUpdater.incrementAndGet(this);
......
boolean discard;
lock.lock();
try {
// 如果當前正在使用的連接數未達到最大連接數
// 則當前正在使用的連接數加1
// 否則銷燬剛剛創建出來的連接
if (activeCount < maxActive) {
activeCount++;
holder.active = true;
if (activeCount > activePeak) {
activePeak = activeCount;
activePeakTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
break;
} else {
discard = true;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
if (discard) {
JdbcUtils.close(pyConnInfo.getPhysicalConnection());
}
}
}
// 上鎖
try {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
connectErrorCountUpdater.incrementAndGet(this);
throw new SQLException("interrupt", e);
}
try {
// maxWaitThreadCount表示允許的最大等待連接的應用線程數
// notEmptyWaitThreadCount表示正在等待連接的應用線程數
// 等待連接的應用線程數達到最大值時,拋出異常
if (maxWaitThreadCount > 0
&& notEmptyWaitThreadCount >= maxWaitThreadCount) {
connectErrorCountUpdater.incrementAndGet(this);
throw new SQLException("maxWaitThreadCount " + maxWaitThreadCount + ", current wait Thread count "
+ lock.getQueueLength());
}
// 發生了致命錯誤,且設置了致命錯誤數最大值大於0,且正在使用的連接數大於等於致命錯誤數最大值
if (onFatalError
&& onFatalErrorMaxActive > 0
&& activeCount >= onFatalErrorMaxActive) {
// 拼接異常並拋出
......
throw new SQLException(
errorMsg.toString(), lastFatalError);
}
connectCount++;
// 如果配置的創建連接的線程池是一個定時線程池
// 且連接池已經沒有可用連接,
// 且當前借出的連接數未達到允許的最大連接數
// 且當前沒有其它線程(應用線程,創建連接的線程,創建連接的線程池裏的線程)在創建連接
// 此時將createDirect置為true,讓當前應用線程直接創建連接
if (createScheduler != null
&& poolingCount == 0
&& activeCount < maxActive
&& creatingCountUpdater.get(this) == 0
&& createScheduler instanceof ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor) {
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor executor = (ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor) createScheduler;
if (executor.getQueue().size() > 0) {
createDirect = true;
continue;
}
}
if (maxWait > 0) {
// 如果設置了等待連接的最大等待時間,則調用pollLast()方法來拿連接
// pollLast()方法執行時如果池中沒有連接,則應用線程會在notEmpty上最多等待maxWait的時間
holder = pollLast(nanos);
} else {
// 調用takeLast()方法拿連接時,如果池中沒有連接,則會在notEmpty上一直等待,直到池中有連接
holder = takeLast();
}
if (holder != null) {
if (holder.discard) {
continue;
}
// 正在使用的連接數加1
activeCount++;
holder.active = true;
if (activeCount > activePeak) {
activePeak = activeCount;
activePeakTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
connectErrorCountUpdater.incrementAndGet(this);
throw new SQLException(e.getMessage(), e);
} catch (SQLException e) {
connectErrorCountUpdater.incrementAndGet(this);
throw e;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
break;
}
// 如果拿到的連接為null,説明拿連接時等待超時了
// 此時拋出連接超時異常
if (holder == null) {
......
final Throwable createError;
try {
lock.lock();
......
createError = this.createError;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
......
if (createError != null) {
throw new GetConnectionTimeoutException(errorMessage, createError);
} else {
throw new GetConnectionTimeoutException(errorMessage);
}
}
holder.incrementUseCount();
DruidPooledConnection poolalbeConnection = new DruidPooledConnection(holder);
return poolalbeConnection;
}getConnectionInternal()方法中拿到連接的方式有三種,如下所示。
- 直接創建連接。需要滿足配置的創建連接的線程池是一個定時線程池,且連接池已經沒有可用連接,且當前借出的連接數未達到允許的最大連接數,且當前沒有其它線程在創建連接;
- 從池中拿連接,並最多等待maxWait的時間。需要設置了maxWait;
- 從池中拿連接,並一直等待直到拿到連接。
下面最後看一下超時等待拿連接的DruidDataSource#pollLast方法的實現。
private DruidConnectionHolder pollLast(long nanos) throws InterruptedException, SQLException {
long estimate = nanos;
for (; ; ) {
if (poolingCount == 0) {
// 如果池中已經沒有連接,則喚醒在empty上等待的創建連接線程來創建連接
emptySignal();
if (failFast && isFailContinuous()) {
throw new DataSourceNotAvailableException(createError);
}
// 等待時間耗盡,返回null
if (estimate <= 0) {
waitNanosLocal.set(nanos - estimate);
return null;
}
// 應用線程即將在下面的notEmpty上等待
// 這裏先把等待獲取連接的應用線程數加1
notEmptyWaitThreadCount++;
if (notEmptyWaitThreadCount > notEmptyWaitThreadPeak) {
notEmptyWaitThreadPeak = notEmptyWaitThreadCount;
}
try {
long startEstimate = estimate;
// 應用線程在notEmpty上等待
// 有連接被創建或者被歸還時,會喚醒在notEmpty上等待的應用線程
estimate = notEmpty.awaitNanos(estimate);
notEmptyWaitCount++;
notEmptyWaitNanos += (startEstimate - estimate);
if (!enable) {
connectErrorCountUpdater.incrementAndGet(this);
if (disableException != null) {
throw disableException;
}
throw new DataSourceDisableException();
}
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
notEmpty.signal();
notEmptySignalCount++;
throw ie;
} finally {
notEmptyWaitThreadCount--;
}
if (poolingCount == 0) {
if (estimate > 0) {
// 若喚醒後池中還是沒有連接,且此時等待時間還有剩餘
// 則重新在notEmpty上等待
continue;
}
waitNanosLocal.set(nanos - estimate);
return null;
}
}
// poolingCount--
decrementPoolingCount();
// 從池中拿到連接
DruidConnectionHolder last = connections[poolingCount];
connections[poolingCount] = null;
long waitNanos = nanos - estimate;
last.setLastNotEmptyWaitNanos(waitNanos);
return last;
}
}五. DruidDataSource連接歸還
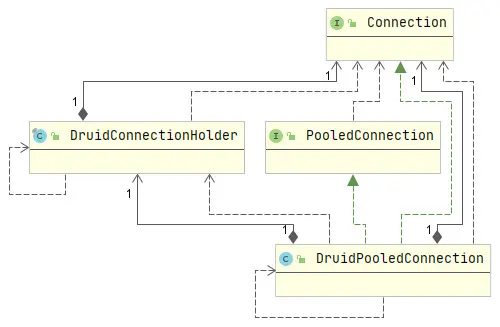
Druid數據庫連接池中,每一個物理連接都會被包裝成DruidConnectionHolder,在提供給應用線程前,還會將DruidConnectionHolder包裝成DruidPooledConnection,類圖如下所示。
應用線程中使用連接完畢後,會調用DruidPooledConnection的close()方法來歸還連接,也就是將連接放回連接池。DruidPooledConnection#close方法如下所示。
public void close() throws SQLException {
if (this.disable) {
return;
}
DruidConnectionHolder holder = this.holder;
if (holder == null) {
if (dupCloseLogEnable) {
LOG.error("dup close");
}
return;
}
DruidAbstractDataSource dataSource = holder.getDataSource();
// 判斷歸還連接的線程和獲取連接的線程是否是同一個線程
boolean isSameThread = this.getOwnerThread() == Thread.currentThread();
// 如果不是同一個線程,則設置asyncCloseConnectionEnable為true
if (!isSameThread) {
dataSource.setAsyncCloseConnectionEnable(true);
}
// 如果開啓了removeAbandoned機制
// 或者asyncCloseConnectionEnable為true
// 則調用syncClose()方法來歸還連接
// syncClose()方法中會先加鎖,然後調用recycle()方法來回收連接
if (dataSource.isAsyncCloseConnectionEnable()) {
syncClose();
return;
}
if (!CLOSING_UPDATER.compareAndSet(this, 0, 1)) {
return;
}
try {
for (ConnectionEventListener listener : holder.getConnectionEventListeners()) {
listener.connectionClosed(new ConnectionEvent(this));
}
List<Filter> filters = dataSource.getProxyFilters();
if (filters.size() > 0) {
FilterChainImpl filterChain = new FilterChainImpl(dataSource);
filterChain.dataSource_recycle(this);
} else {
// 回收連接
recycle();
}
} finally {
CLOSING_UPDATER.set(this, 0);
}
this.disable = true;
}在DruidPooledConnection#close方法中,會先判斷本次歸還連接的線程和獲取連接的線程是否是同一個線程,如果不是,則先加鎖然後再調用recycle()方法來回收連接,如果是則直接調用recycle()方法來回收連接。當開啓了removeAbandoned機制時,就可能會出現歸還連接的線程和獲取連接的線程不是同一個線程的情況,這是因為一旦開啓了removeAbandoned機制,那麼每一個被借出的連接都會被放到activeConnections活躍連接map中,並且在銷燬連接的線程DestroyConnectionThread中會每間隔timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis的時間就遍歷一次activeConnections活躍連接map,一旦有活躍連接被借出的時間大於了removeAbandonedTimeoutMillis,那麼銷燬連接的線程DestroyConnectionThread就會主動去回收這個連接,以防止連接泄漏。
下面看一下DruidPooledConnection#recycle方法的實現。
public void recycle() throws SQLException {
if (this.disable) {
return;
}
DruidConnectionHolder holder = this.holder;
if (holder == null) {
if (dupCloseLogEnable) {
LOG.error("dup close");
}
return;
}
if (!this.abandoned) {
DruidAbstractDataSource dataSource = holder.getDataSource();
// 調用DruidAbstractDataSource#recycle回收當前連接
dataSource.recycle(this);
}
this.holder = null;
conn = null;
transactionInfo = null;
closed = true;
}在DruidPooledConnection#recycle方法中會調用到DruidDataSource#recycle方法來回收連接。DruidDataSource#recycle方法實現如下所示。
protected void recycle(DruidPooledConnection pooledConnection) throws SQLException {
final DruidConnectionHolder holder = pooledConnection.holder;
......
final boolean isAutoCommit = holder.underlyingAutoCommit;
final boolean isReadOnly = holder.underlyingReadOnly;
final boolean testOnReturn = this.testOnReturn;
try {
// 如果是非自動提交且存在事務
// 則回滾事務
if ((!isAutoCommit) && (!isReadOnly)) {
pooledConnection.rollback();
}
// 重置連接信息(配置還原為默認值,關閉Statement,清除連接的Warnings等)
boolean isSameThread = pooledConnection.ownerThread == Thread.currentThread();
if (!isSameThread) {
final ReentrantLock lock = pooledConnection.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
holder.reset();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} else {
holder.reset();
}
......
// 開啓了testOnReturn機制,則校驗連接有效性
if (testOnReturn) {
boolean validate = testConnectionInternal(holder, physicalConnection);
// 校驗不通過則關閉物理連接
if (!validate) {
JdbcUtils.close(physicalConnection);
destroyCountUpdater.incrementAndGet(this);
lock.lock();
try {
if (holder.active) {
activeCount--;
holder.active = false;
}
closeCount++;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return;
}
}
......
lock.lock();
try {
// 連接即將放回連接池,需要將active設置為false
if (holder.active) {
activeCount--;
holder.active = false;
}
closeCount++;
// 將連接放到connections數組的poolingCount位置
// 然後poolingCount加1
// 然後喚醒在notEmpty上等待連接的一個應用線程
result = putLast(holder, currentTimeMillis);
recycleCount++;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
if (!result) {
JdbcUtils.close(holder.conn);
LOG.info("connection recyle failed.");
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
......
}
}DruidDataSource#recycle方法中會先重置連接信息,即將連接的一些配置重置為默認值,然後關閉連接的Statement和Warnings,如果開啓了testOnReturn機制,則還需要校驗一下連接的有效性,校驗不通過則直接關閉物理連接,最後,將連接放回到connections數組的poolingCount位置,然後喚醒一個在notEmpty上等待連接的應用線程。
六. removeAbandoned機制
Druid數據庫連接池提供了removeAbandoned機制來防止連接泄漏。要開啓removeAbandoned機制,需要設置如下參數。
| 參數 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| removeAbandoned | 發生連接泄漏時,是否需要回收泄漏的連接。默認為false,表示不回收。 |
| removeAbandonedTimeoutMillis | 判斷髮生連接泄漏的超時時間。默認為300秒。 |
下面將對開啓removeAbandoned機制後,如何回收發生了泄漏的連接進行説明。當應用線程從連接池獲取到一個連接後,如果開啓了removeAbandoned機制,那麼會將這個連接放到activeConnections活躍連接map中,對應的方法為DruidDataSource#getConnectionDirect,源碼片段如下所示。
public DruidPooledConnection getConnectionDirect(long maxWaitMillis) throws SQLException {
int notFullTimeoutRetryCnt = 0;
for (; ; ) {
DruidPooledConnection poolableConnection;
......
if (removeAbandoned) {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = Thread.currentThread().getStackTrace();
poolableConnection.connectStackTrace = stackTrace;
// 設置connectedTimeNano,用於後續判斷連接借出時間是否大於removeAbandonedTimeoutMillis
poolableConnection.setConnectedTimeNano();
poolableConnection.traceEnable = true;
activeConnectionLock.lock();
try {
// 將從連接池獲取到的連接放到activeConnections中
activeConnections.put(poolableConnection, PRESENT);
} finally {
activeConnectionLock.unlock();
}
}
if (!this.defaultAutoCommit) {
poolableConnection.setAutoCommit(false);
}
return poolableConnection;
}
}又已知Druid數據庫連接池有一個銷燬連接的線程會每間隔timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis執行一次DestroyTask#run方法來銷燬連接,DestroyTask#run方法如下所示。
public void run() {
shrink(true, keepAlive);
// 如果開啓了removeAbandoned機制
// 則執行removeAbandoned()方法來檢測發生了泄漏的連接並回收
if (isRemoveAbandoned()) {
removeAbandoned();
}
}DestroyTask#run方法的最後會判斷是否開啓了removeAbandoned機制,如果開啓了則會執行DruidDataSource#removeAbandoned方法來檢測哪些連接發生了泄漏,並主動回收這些連接。DruidDataSource#removeAbandoned方法如下所示。
public int removeAbandoned() {
int removeCount = 0;
long currrentNanos = System.nanoTime();
List<DruidPooledConnection> abandonedList = new ArrayList<DruidPooledConnection>();
activeConnectionLock.lock();
try {
Iterator<DruidPooledConnection> iter = activeConnections.keySet().iterator();
for (; iter.hasNext(); ) {
DruidPooledConnection pooledConnection = iter.next();
// 運行中的連接不會被判定為發生了泄漏
if (pooledConnection.isRunning()) {
continue;
}
long timeMillis = (currrentNanos - pooledConnection.getConnectedTimeNano()) / (1000 * 1000);
// 判斷連接借出時間是否達到連接泄漏的超時時間
if (timeMillis >= removeAbandonedTimeoutMillis) {
// 將發生了泄漏的連接從activeConnections中移除
iter.remove();
pooledConnection.setTraceEnable(false);
// 將發生了泄露的連接添加到abandonedList集合中
abandonedList.add(pooledConnection);
}
}
} finally {
activeConnectionLock.unlock();
}
if (abandonedList.size() > 0) {
// 遍歷abandonedList集合
// 主動調用每個發生了泄漏的DruidPooledConnection的close()方法來回收連接
for (DruidPooledConnection pooledConnection : abandonedList) {
final ReentrantLock lock = pooledConnection.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (pooledConnection.isDisable()) {
continue;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
JdbcUtils.close(pooledConnection);
pooledConnection.abandond();
removeAbandonedCount++;
removeCount++;
......
}
}
return removeCount;
}DruidDataSource#removeAbandoned方法中主要完成的事情就是將每個發生了泄漏的連接從activeConnections中移動到abandonedList中,然後遍歷abandonedList中的每個連接並調用DruidPooledConnection#close方法,最終完成泄漏連接的回收。
總結
Druid數據庫連接池中,應用線程向連接池獲取連接時,如果池中沒有連接,則應用線程會在notEmpty上等待,同時Druid數據庫連接池中有一個創建連接的線程,會持續的向連接池創建連接,如果連接池已滿,則創建連接的線程會在empty上等待。
當有連接被生產,或者有連接被歸還,會喚醒在notEmpty上等待的應用線程,同理有連接被銷燬時,會喚醒在empty上等待的生產連接的線程。
Druid數據庫連接池中還有一個銷燬連接的線程,會每間隔timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis的時間執行一次DestroyTask任務來銷燬連接,這些被銷燬的連接可以是存活時間達到最大值的連接,也可以是空閒時間達到指定值的連接。如果還開啓了保活機制,那麼空閒時間大於keepAliveBetweenTimeMillis的連接都會被校驗一次有效性,校驗不通過的連接會被銷燬。
最後,Druid數據庫連接池提供了removeAbandoned機制來防止連接泄漏,當開啓了removeAbandoned機制時,每一個被應用線程獲取的連接都會被添加到activeConnections活躍連接map中,如果這個連接在應用線程中使用完畢後沒有被關閉,那麼Druid數據庫連接池會從activeConnections中將其識別出來並主動回收。
大家好,我是半夏之沫 😁😁 一名金融科技領域的JAVA系統研發😊😊
我希望將自己工作和學習中的經驗以最樸實,最嚴謹的方式分享給大家,共同進步👉💓👈
👉👉👉👉👉👉👉👉💓寫作不易,期待大家的關注和點贊💓👈👈👈👈👈👈👈👈
👉👉👉👉👉👉👉👉💓關注微信公眾號【技術探界】 💓👈👈👈👈👈👈👈👈