作者:劉晨
網名 bisal ,具有十年以上的應用運維工作經驗,目前主要從事數據庫應用研發能力提升和技術管理相關的工作,Oracle ACE ,騰訊雲TVP,擁有 Oracle OCM & OCP 、EXIN DevOps Master 、SCJP 等國際認證,國內首批 Oracle YEP 成員,OCMU 成員,《DevOps 最佳實踐》中文譯者之一,CSDN & ITPub 專家博主,公眾號"bisal的個人雜貨鋪",長期堅持分享技術文章,多次在線上和線下分享技術主題。
本文來源:原創投稿
*愛可生開源社區出品,原創內容未經授權不得隨意使用,轉載請聯繫小編並註明來源。
同事提了個問題,某套5.7的MySQL,新建一個只讀的用户,執行如下操作,
create user 'readuser'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'readuser';
GRANT SELECT ON *.* TO 'readuser'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY "readuser";但是當使用該用户登錄的時候,
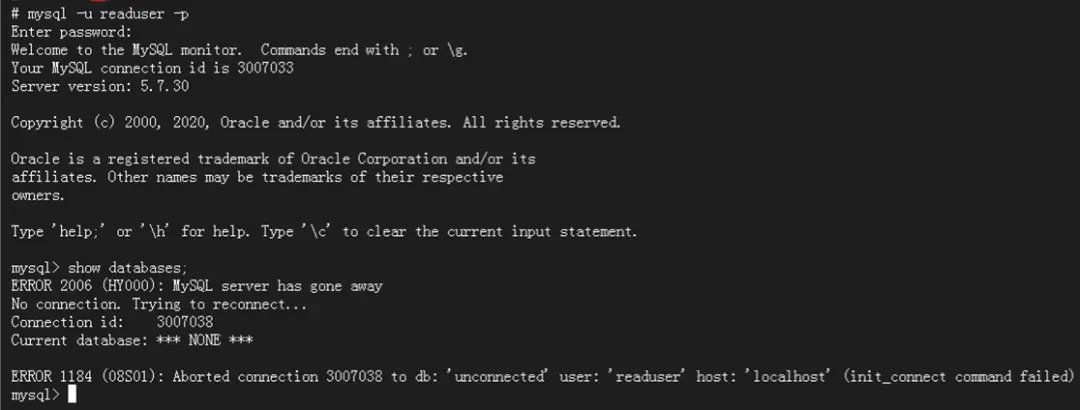
mysql -ureaduser -preader提示"MySQL server has gone away",很詭異的一個錯,以前沒碰到過:
其他現象,
- MySQL進程存在。
- 使用root賬號,可以正常登錄。
- 通過TCP/IP登錄該用户,仍然報錯,
mysql -ureaduser -preaduser -h127.0.0.1 -P3306官方文檔談到了這個錯誤,
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/ref...
P. S. 這篇文章翻譯了一下,可以參考,
https://blog.csdn.net/ldlovem...
B.3.2.7 MySQL server has gone away
This section also covers the related Lost connection to server during query error.
The most common reason for the MySQL server has gone away error is that the server timed out and closed the connection. In this case, you normally get one of the following error codes (which one you get is operating system-dependent).

If you have a script, you just have to issue the query again for the client to do an automatic reconnection. This assumes that you have automatic reconnection in the client enabled (which is the default for the mysql command-line client).Some other common reasons for the MySQL server has gone away error are:
-You (or the db administrator) has killed the running thread with a KILL statement or a mysqladmin kill command.
-You tried to run a query after closing the connection to the server. This indicates a logic error in the application that should be corrected.
-A client application running on a different host does not have the necessary privileges to connect to the MySQL server from that host.
-You got a timeout from the TCP/IP connection on the client side.
This may happen if you have been using the commands:
mysql_options(…, MYSQL_OPT_READ_TIMEOUT,…)
or mysql_options(…, MYSQL_OPT_WRITE_TIMEOUT,…). In this case increasing the timeout may help solve the problem.
-You have encountered a timeout on the server side and the automatic reconnection in the client is disabled (the reconnect flag in the MYSQL structure is equal to 0).
-You are using a Windows client and the server had dropped the connection (probably because wait_timeout expired) before the command was issued.
The problem on Windows is that in some cases MySQL does not get an error from the OS when writing to the TCP/IP connection to the server, but instead gets the error when trying to read the answer from the connection.
The solution to this is to either do a mysql_ping() on the connection if there has been a long time since the last query (this is what Connector/ODBC does) or set wait_timeout on the mysqld server so high that it in practice never times out.
-You can also get these errors if you send a query to the server that is incorrect or too large. If mysqld receives a packet that is too large or out of order, it assumes that something has gone wrong with the client and closes the connection. If you need big queries (for example, if you are working with big BLOB columns), you can increase the query limit by setting the server's max_allowed_packet variable, which has a default value of 4MB. You may also need to increase the maximum packet size on the client end. More information on setting the packet size is given in Section B.3.2.8, “Packet Too Large”.
An INSERT or REPLACE statement that inserts a great many rows can also cause these sorts of errors. Either one of these statements sends a single request to the server irrespective of the number of rows to be inserted; thus, you can often avoid the error by reducing the number of rows sent per INSERT or REPLACE.
-It is also possible to see this error if host name lookups fail (for example, if the DNS server on which your server or network relies goes down). This is because MySQL is dependent on the host system for name resolution, but has no way of knowing whether it is working—from MySQL's point of view the problem is indistinguishable from any other network timeout.
You may also see the MySQL server has gone away error if MySQL is started with the skip_networking system variable enabled.
Another networking issue that can cause this error occurs if the MySQL port (default 3306) is blocked by your firewall, thus preventing any connections at all to the MySQL server.
-You can also encounter this error with applications that fork child processes, all of which try to use the same connection to the MySQL server. This can be avoided by using a separate connection for each child process.
-You have encountered a bug where the server died while executing the query.
You can check whether the MySQL server died and restarted by executing mysqladmin version and examining the server's uptime. If the client connection was broken because mysqld crashed and restarted, you should concentrate on finding the reason for the crash. Start by checking whether issuing the query again kills the server again. See Section B.3.3.3, “What to Do If MySQL Keeps Crashing”.
You can obtain more information about lost connections by starting mysqld with the log_error_verbosity system variable set to 3. This logs some of the disconnection messages in the hostname.err file. See Section 5.4.2, “The Error Log”.
If you want to create a bug report regarding this problem, be sure that you include the following information:
-Indicate whether the MySQL server died. You can find information about this in the server error log. See Section B.3.3.3, “What to Do If MySQL Keeps Crashing”.-If a specific query kills mysqld and the tables involved were checked with CHECK TABLE before you ran the query, can you provide a reproducible test case? See Section 5.8, “Debugging MySQL”.
-What is the value of the wait_timeout system variable in the MySQL server? (mysqladmin variables gives you the value of this variable.)
-Have you tried to run mysqld with the general query log enabled to determine whether the problem query appears in the log? (See Section 5.4.3, “The General Query Log”.)
但是逐一排查,沒出現特別對應的場景。
查了一些資料,説是給新增用户一個super權限,嘗試了下,確實能解決,但這相當於給用户一個超級權限,不符合只讀賬號的需求,
grant super on *.* TO 'readuser'@'%';這是因為什麼?
知其然,更要知其所以然。
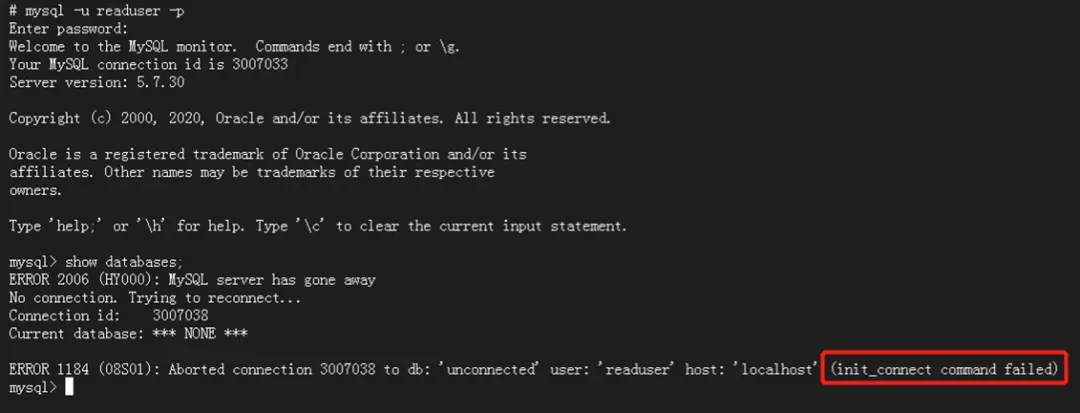
再看下當時的錯誤提示,"init_connect command failed"引起了注意:
他其實是MySQL的參數,一般默認為空,但此處值是'SET NAMES utf8mb4',請注意,此處有個''單引號,
> show variables like '%init_connect%';
+---------------+---------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+---------------------+
| init_connect | 'SET NAMES utf8mb4' |
+---------------+---------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)init_connect參數的作用,官方文檔有説明,
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/ref...
大概意思是,
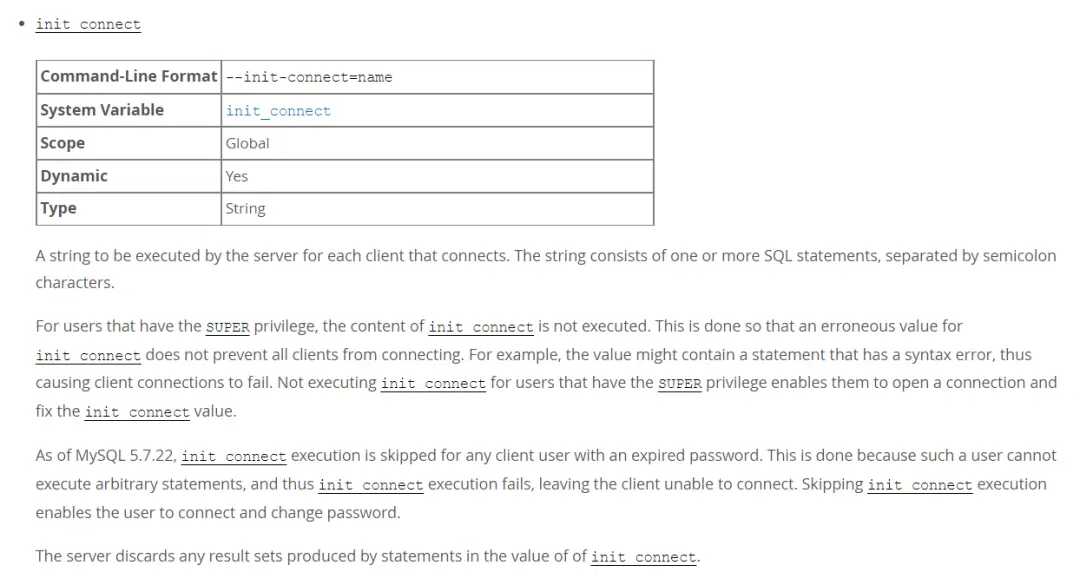
- 這個參數可以包括一條或者多條SQL語句,用分號隔開,他是每個連接到數據庫的客户端都需要執行的指令。
- 但是對具有SUPER權限用户,會忽略這個init_connect,不會執行其中的指令。
- 如果init_connect中包含的語句存在語法錯誤,則會導致客户端連接失敗。
- 只能通過具有SUPER權限用户來修改init_connect的值。
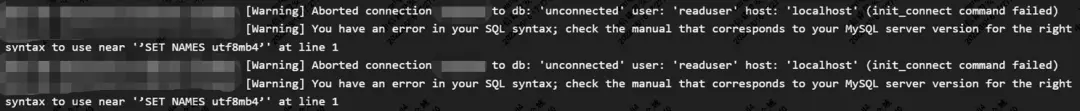
如上環境中init_connect設置的值是'SET NAMES utf8mb4',如果我們直接執行這個指令,提示存在語法上的錯誤,
> 'SET NAMES utf8mb4';
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near ''SET NAMES utf8mb4'' at line 1為了驗證,從MySQL的error日誌,能看到這些信息,和上述操作的錯誤提示相同,破案了:
解決方案就很直接了,設置正確的init_connect,就無需給新建用户授予super權限,都可以正常登錄,
set global init_connect = "set names utf8mb4";説起這個參數,可能有些DBA用它來做一些特殊的用途,例如對某些業務賬號的限制等,所有非super權限賬號都會執行一次,而具有super權限的賬號或者DBA賬號(通常有super的權限),登錄不會執行init_connect設置的指令。所以針對這個案例來説,很可能在數據庫初始化的時候,init_connect就設置錯了,但是一直用的是超級賬號,只有當創建非super賬號的時候,才會暴露這問題。
因此,應急場景下,優先解決問題,但是對問題的根源,還是要充分了解,只有這樣,才能舉一反三,提高自己的能力。