<div>
</div>
1. 引言
在本教程中,我們將學習如何使用 Spring 配置 Apache Kafka 的死信隊列(Dead Letter Queue)機制。
2. 死信隊列 (Dead Letter Queues)
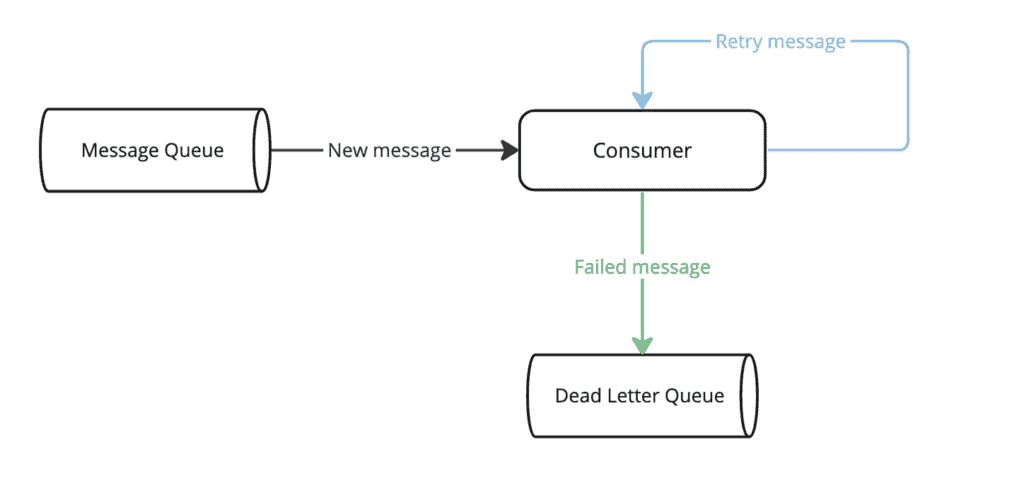
3. Spring Kafka 中的死信隊列
在 Spring Kafka 中,死信隊列 (DLT) 是 Dead Letter Queue (DLQ) 概念的對應實現。 在後續章節中,我們將通過一個簡單的支付系統來觀察 DLT 機制的工作原理。
3.1. 模型類
讓我們從模型類開始:
public class Payment {
private String reference;
private BigDecimal amount;
private Currency currency;
// standard getters and setters
}讓我們也實現一個用於創建事件的實用方法:
static Payment createPayment(String reference) {
Payment payment = new Payment();
payment.setAmount(BigDecimal.valueOf(71));
payment.setCurrency(Currency.getInstance("GBP"));
payment.setReference(reference);
return payment;
}<div>
<h1>Introduction</h1>
<p>This document provides an overview of the new API. It covers key features, usage examples, and troubleshooting tips.</p>
<h2>Key Features</h2>
<ul>
<li><strong>Data Validation:</strong> Ensures data integrity by validating input against predefined schemas.</li>
<li><strong>Asynchronous Operations:</strong> Supports asynchronous operations for improved performance and responsiveness.</li>
<li><strong>Error Handling:</strong> Provides robust error handling mechanisms with detailed error codes and messages.</li>
</ul>
<h2>Usage Examples</h2>
<pre><code>
function fetchData(url) {
return fetch(url)
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
console.log(data);
return data;
})
.catch(error => {
console.error("Error fetching data:", error);
return null;
});
}
// Example usage:
// fetchData("https://example.com/api/data");
</code></pre>
<p>The code above demonstrates how to fetch data from a remote API endpoint.</p>
<h2>Troubleshooting</h2>
<p>If you encounter any issues, please refer to the following troubleshooting steps:</p>
<ul>
<li><strong>Check Network Connectivity:</strong> Ensure you have a stable internet connection.</li>
<li><strong>Verify API Endpoint:</strong> Confirm the API endpoint URL is correct.</li>
<li><strong>Inspect Response Headers:</strong> Examine the response headers for any error codes or messages.</li>
</ul>
</div>
3.2. 環境搭建
接下來,我們需要添加所需的依賴項:spring-kafka 和 jackson-databind。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
<version>3.1.2</version> </dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.14.3</version>
</dependency>我們現在可以創建 ConsumerFactory 和 ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory 兩個 Bean:
@Bean
public ConsumerFactory<String, Payment> consumerFactory() {
Map<String, Object> config = new HashMap<>();
config.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, bootstrapServers);
return new DefaultKafkaConsumerFactory<>(
config, new StringDeserializer(), new JsonDeserializer<>(Payment.class));
}
@Bean
public ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<String, Payment> containerFactory() {
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<String, Payment> factory =
new ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<>();
factory.setConsumerFactory(consumerFactory());
return factory;
}<p>最後,我們來實施主要主題的消費者:</p>
@KafkaListener(topics = { "payments" }, groupId = "payments")
public void handlePayment(
Payment payment, @Header(KafkaHeaders.RECEIVED_TOPIC) String topic) {
log.info("Event on main topic={}, payload={}", topic, payment);
}在繼續討論DLT示例之前,我們先討論一下重試配置。
3.3. 關閉重試
在實際項目中,在發生錯誤時重試處理事件並將其發送到 DLT 是一種常見做法。 這可以通過 Spring Kafka 提供的非阻塞重試機制輕鬆實現。
然而,在本文中,我們將關閉重試功能,以突出顯示 DLT 機制。 當主主題的消費者無法處理事件時,事件將直接發佈到 DLT。
首先,我們需要定義 producerFactory 和 retryableTopicKafkaTemplate Bean:
@Bean
public ProducerFactory<String, Payment> producerFactory() {
Map<String, Object> config = new HashMap<>();
config.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, bootstrapServers);
return new DefaultKafkaProducerFactory<>(
config, new StringSerializer(), new JsonSerializer<>());
}
@Bean
public KafkaTemplate<String, Payment> retryableTopicKafkaTemplate() {
return new KafkaTemplate<>(producerFactory());
}現在我們可以定義主話題的消費者,無需額外的重試,正如之前所述:
@RetryableTopic(attempts = "1", kafkaTemplate = "retryableTopicKafkaTemplate")
@KafkaListener(topics = { "payments"}, groupId = "payments")
public void handlePayment(
Payment payment, @Header(KafkaHeaders.RECEIVED_TOPIC) String topic) {
log.info("Event on main topic={}, payload={}", topic, payment);
}<div>
<p><strong>在 <em title="@RetryableTopic">@RetryableTopic</em> 註解中,<em title="attempts">attempts</em> 屬性表示在將消息發送到 DLT 之前嘗試的次數。</strong></p>
4. 配置死信主題
現在我們準備好實施 DL 消費者:

