1. 引言
通常在使用大型語言模型 (LLM) 時,我們並不能期望獲得結構化的響應。此外,我們已經習慣了它們不可預測的行為,這常常導致輸出不符合我們的預期。然而,也有方法可以增加生成結構化響應的可能性(雖然並非 100% 概率),甚至將這些響應解析為可用的代碼結構。
在本教程中,我們將探索 Spring AI 以及簡化和優化這一過程的工具,使其更易於訪問和操作。
2. 聊天模型簡介
允許我們向 AI 模型發送提示的基本結構是 ChatModel 接口:
public interface ChatModel extends Model<Prompt, ChatResponse> {
default String call(String message) {
// implementation is skipped
}
@Override
ChatResponse call(Prompt prompt);
}call() 方法的作用是向模型發送消息並接收響應,除此之外沒有任何其他功能。 期望提示和響應為 String 類型是自然的。 然而,現代模型實現通常具有更復雜的結構,從而實現更精細的調整,提高模型的可預測性。 例如,雖然默認的 call() 方法接受 String 參數是可用的,但使用 Prompt 更加實用。 這個 Prompt 可以包含多個消息或包括温度等選項,以調節模型的顯式創造性。
我們可以自動注入 ChatModel 並直接調用它。 例如,如果我們的依賴項中包含 spring-ai-openai-spring-boot-starter 用於 OpenAI API,則 OpenAiChatModel 實現將被自動注入。
3. 結構化輸出 API
為了以數據結構的形式獲取輸出,Spring AI 提供工具來使用結構化輸出 API 包裹 ChatModel 的調用。 此 API 的核心接口是 StructuredOutputConverter:
public interface StructuredOutputConverter<T> extends Converter<String, T>, FormatProvider {}它結合了兩個其他接口,第一個是 FormatProvider:
public interface FormatProvider {
String getFormat();
}
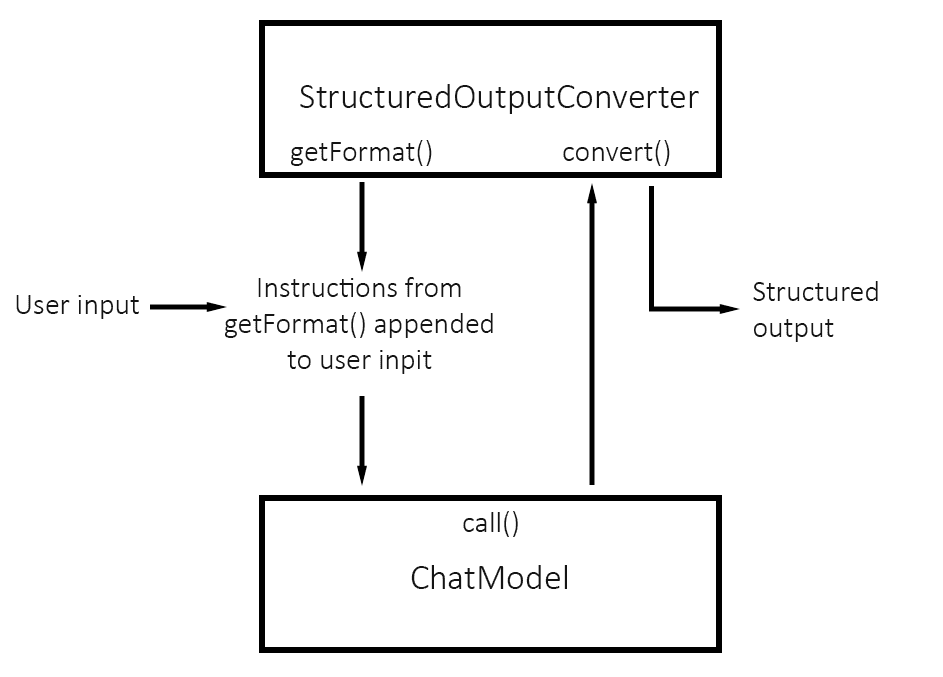
在 <em style="font-style: italic;">ChatModel’</em 的 <em style="font-style: italic;">call()</em 方法執行之前,<em style="font-style: italic;">getFormat()</em 會準備提示語,並將其填充所需的數據模式,並明確説明數據應如何格式化,以避免響應中的不一致性。例如,為了獲得 JSON 格式的響應,它會使用以下提示語:</p>
public String getFormat() {
String template = "Your response should be in JSON format.\n"
+ "Do not include any explanations, only provide a RFC8259 compliant JSON response following this format without deviation.\n"
+ "Do not include markdown code blocks in your response.\n
+ "Remove the ```json markdown from the output.\nHere is the JSON Schema instance your output must adhere to:\n```%s```\n";
return String.format(template, this.jsonSchema);
}這些説明通常在用户輸入之後添加。
第二界面是 轉換器:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Converter<S, T> {
@Nullable
T convert(S source);
// default method
}
在 call() 返回響應後,轉換器會將它解析為類型 T 的所需數據結構。以下是 StructuredOutputConverter 的簡單流程圖:
4. 可用轉換器
本節將探討 <em>StructuredOutputConverter</em> 的可用實現方案,並提供示例。我們將通過生成用於《龍與地下城》遊戲的字符來演示這一點:
public class Character {
private String name;
private int age;
private String race;
private String characterClass;
private String cityOfOrigin;
private String favoriteWeapon;
private String bio;
// constructor, getters, and setters
}<p><strong>請注意,由於 Jackson 的 <em >ObjectMapper</em> 在幕後使用,因此我們需要為我們的 Bean 提供空構造函數。</strong></p>
5. BeanOutputConverter 用於 Bean 對象
BeanOutputConverter 負責從模型響應中生成指定類的一個實例。 它會構造一個提示,用於指導模型生成符合 RFC8259 規範的 JSON。 讓我們通過 ChatClient API 來看如何使用它:
@Override
public Character generateCharacterChatClient(String race) {
return ChatClient.create(chatModel).prompt()
.user(spec -> spec.text("Generate a D&D character with race {race}")
.param("race", race))
.call()
.entity(Character.class); // <-------- we call ChatModel.call() here, not on the line before
}此方法中, 實例化了一個 。 方法啓動了構建鏈,並傳入請求 ()。 在我們的例子中,我們只添加了用户的文本。 請求創建後,調用 方法,返回一個新的 ,其中包含 和 。 方法則基於提供的類型創建轉換器,完成提示,並調用 AI 模型。
我們可能會注意到,我們沒有直接使用 。 這是因為我們使用一個類作為 方法的參數,這意味着 會處理提示和轉換。
為了獲得更大的控制權,我們可以編寫低級別的實現方式。 在這裏,我們將使用 ,該方法我們已經進行了自動注入:
@Override
public Character generateCharacterChatModel(String race) {
BeanOutputConverter<Character> beanOutputConverter = new BeanOutputConverter<>(Character.class);
String format = beanOutputConverter.getFormat();
String template = """
Generate a D&D character with race {race}
{format}
""";
PromptTemplate promptTemplate = new PromptTemplate(template, Map.of("race", race, "format", format));
Prompt prompt = new Prompt(promptTemplate.createMessage());
Generation generation = chatModel.call(prompt).getResult();
return beanOutputConverter.convert(generation.getOutput().getContent());
}在上面的示例中,我們創建了 BeanOutputConverter,提取了模型格式化指南,然後將這些指南添加到自定義提示中。我們使用 PromptTemplate 生產最終提示。 PromptTemplate 是 Spring AI 的核心提示模板組件,它在底層使用 StringTemplate 引擎。然後,我們調用模型以獲得 Generation 作為結果。 Generation 表示模型的響應:我們提取其內容,然後使用轉換器將其轉換為 Java 對象。
以下是使用我們的轉換器從 OpenAI 獲得的真實響應示例:
{
name: "Thoren Ironbeard",
age: 150,
race: "Dwarf",
characterClass: "Wizard",
cityOfOrigin: "Sundabar",
favoriteWeapon: "Magic Staff",
bio: "Born and raised in the city of Sundabar, he is known for his skills in crafting and magic."
}矮人法師,真是難得一見!
2. 使用 MapOutputConverter 和 ListOutputConverter 處理集合
MapOutputConverter 和 ListOutputConverter 允許我們創建結構化的響應,分別以 Map 和 List 格式呈現。 下面是使用 MapOutputConverter 的高層和底層代碼示例:
@Override
public Map<String, Object> generateMapOfCharactersChatClient(int amount) {
return ChatClient.create(chatModel).prompt()
.user(u -> u.text("Generate {amount} D&D characters, where key is a character's name")
.param("amount", String.valueOf(amount)))
.call()
.entity(new ParameterizedTypeReference<Map<String, Object>>() {});
}
@Override
public Map<String, Object> generateMapOfCharactersChatModel(int amount) {
MapOutputConverter outputConverter = new MapOutputConverter();
String format = outputConverter.getFormat();
String template = """
"Generate {amount} of key-value pairs, where key is a "Dungeons and Dragons" character name and value (String) is his bio.
{format}
""";
Prompt prompt = new Prompt(new PromptTemplate(template, Map.of("amount", String.valueOf(amount), "format", format)).createMessage());
Generation generation = chatModel.call(prompt).getResult();
return outputConverter.convert(generation.getOutput().getContent());
}我們使用 Object 在 Map<String, Object> 中的原因是,目前 MapOutputConverter 不支持泛型值。但別擔心,稍後我們將構建自定義轉換器以支持它。 稍後,讓我們查看 ListOutputConverter 的示例,我們可以在其中自由使用泛型:
@Override
public List<String> generateListOfCharacterNamesChatClient(int amount) {
return ChatClient.create(chatModel).prompt()
.user(u -> u.text("List {amount} D&D character names")
.param("amount", String.valueOf(amount)))
.call()
.entity(new ListOutputConverter(new DefaultConversionService()));
}
@Override
public List<String> generateListOfCharacterNamesChatModel(int amount) {
ListOutputConverter listOutputConverter = new ListOutputConverter(new DefaultConversionService());
String format = listOutputConverter.getFormat();
String userInputTemplate = """
List {amount} D&D character names
{format}
""";
PromptTemplate promptTemplate = new PromptTemplate(userInputTemplate,
Map.of("amount", amount, "format", format));
Prompt prompt = new Prompt(promptTemplate.createMessage());
Generation generation = chatModel.call(prompt).getResult();
return listOutputConverter.convert(generation.getOutput().getContent());
}7. 轉換器解剖或如何構建我們的自定義轉換器
讓我們創建一個轉換器,將來自 AI 模型的元數據轉換為 <em >Map<String, V></em >> 格式,其中V>是一個泛型類型。 類似於 Spring 提供的轉換器,我們的容器將實現StructuredOutputConverter<T>>,這需要我們添加convert()>和getFormat():>` 方法。
public class GenericMapOutputConverter<V> implements StructuredOutputConverter<Map<String, V>> {
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper; // to convert response
private final String jsonSchema; // schema for the instructions in getFormat()
private final TypeReference<Map<String, V>> typeRef; // type reference for object mapper
public GenericMapOutputConverter(Class<V> valueType) {
this.objectMapper = this.getObjectMapper();
this.typeRef = new TypeReference<>() {};
this.jsonSchema = generateJsonSchemaForValueType(valueType);
}
public Map<String, V> convert(@NonNull String text) {
try {
text = trimMarkdown(text);
return objectMapper.readValue(text, typeRef);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to convert JSON to Map<String, V>", e);
}
}
public String getFormat() {
String raw = "Your response should be in JSON format.\nThe data structure for the JSON should match this Java class: %s\n" +
"For the map values, here is the JSON Schema instance your output must adhere to:\n```%s```\n" +
"Do not include any explanations, only provide a RFC8259 compliant JSON response following this format without deviation.\n";
return String.format(raw, HashMap.class.getName(), this.jsonSchema);
}
private ObjectMapper getObjectMapper() {
return JsonMapper.builder()
.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false)
.build();
}
private String trimMarkdown(String text) {
if (text.startsWith("```json") && text.endsWith("```")) {
text = text.substring(7, text.length() - 3);
}
return text;
}
private String generateJsonSchemaForValueType(Class<V> valueType) {
try {
JacksonModule jacksonModule = new JacksonModule();
SchemaGeneratorConfig config = new SchemaGeneratorConfigBuilder(SchemaVersion.DRAFT_2020_12, OptionPreset.PLAIN_JSON)
.with(jacksonModule)
.build();
SchemaGenerator generator = new SchemaGenerator(config);
JsonNode jsonNode = generator.generateSchema(valueType);
ObjectWriter objectWriter = new ObjectMapper().writer(new DefaultPrettyPrinter()
.withObjectIndenter(new DefaultIndenter().withLinefeed(System.lineSeparator())));
return objectWriter.writeValueAsString(jsonNode);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Could not generate JSON schema for value type: " + valueType.getName(), e);
}
}
}<p>如我們所知,<em >getFormat()</em > 提供給 AI 模型的一條指令,它會遵循最終請求 AI 模型中的用户提示。這條指令指定了一個映射結構,併為我們的自定義對象提供模式。我們使用 <em >com.github.victools.jsonschema</em > 庫生成了這個模式。Spring AI 已經內部使用這個庫進行轉換,這意味着我們不需要顯式導入它。</p>
<p>由於我們要求以 JSON 格式返回響應,在 <em >convert()</em > 中,我們使用 Jackson 的 <em >ObjectMapper</em > 進行解析。因此,<span >我們像 Spring 的實現一樣,去除 markdown,以避免 <em >BeanOutputConverter</em > 中出現的異常。</span> AI 模型通常使用 markdown 來包圍代碼片段,通過去除它,我們避免了 <em >ObjectMapper</em > 引起的異常。</p>
<p>之後,我們可以使用我們的實現方式如下:</p>
@Override
public Map<String, Character> generateMapOfCharactersCustomConverter(int amount) {
GenericMapOutputConverter<Character> outputConverter = new GenericMapOutputConverter<>(Character.class);
String format = outputConverter.getFormat();
String template = """
"Generate {amount} of key-value pairs, where key is a "Dungeons and Dragons" character name and value is character object.
{format}
""";
Prompt prompt = new Prompt(new PromptTemplate(template, Map.of("amount", String.valueOf(amount), "format", format)).createMessage());
Generation generation = chatModel.call(prompt).getResult();
return outputConverter.convert(generation.getOutput().getContent());
}
@Override
public Map<String, Character> generateMapOfCharactersCustomConverterChatClient(int amount) {
return ChatClient.create(chatModel).prompt()
.user(u -> u.text("Generate {amount} D&D characters, where key is a character's name")
.param("amount", String.valueOf(amount)))
.call()
.entity(new GenericMapOutputConverter<>(Character.class));
}8. 結論
在本文中,我們探討了如何使用大型語言模型 (LLM) 生成結構化響應。通過利用 <em >StructuredOutputConverter</em>,我們可以高效地將模型的輸出轉換為可用的數據結構。隨後,我們討論了 <em >BeanOutputConverter</em>、<em >MapOutputConverter</em> 和 <em >ListOutputConverter</em> 的使用案例,並提供了每個案例的實用示例。此外,我們還深入研究了創建自定義轉換器以處理更復雜的數據類型。藉助這些工具,將人工智能驅動的結構化輸出集成到 Java 應用程序中變得更加容易和可管理,從而增強 LLM 響應的可靠性和可預測性。

