1. 概述
安全在 REST API 開發中起着至關重要的作用。一個不安全的 REST API 可能會直接提供對後端系統敏感數據的訪問。因此,組織需要關注 API 安全。 Spring Security 提供各種機制來安全我們的 REST API。其中之一是 API 密鑰。API 密鑰是一個客户端在調用 API 調用時提供的令牌。 在本教程中,我們將討論 Spring Security 中基於 API 密鑰的身份驗證的實現。
2. REST API 安全
Spring Security 可用於保護 REST API。 REST API 具有無狀態特性。因此,它們不應使用會話或 Cookie。相反,應使用基本身份驗證、API 密鑰、JWT 或基於 OAuth2 的令牌進行安全保護。
2.1. 基本身份驗證
基本身份驗證是一種簡單的身份驗證方案。客户端通過發送帶有 Authorization 標頭的 HTTP 請求,該標頭包含單詞 Basic,後跟一個空格以及 Base64 編碼的字符串 username:password。基本身份驗證只有與其他安全機制(如 HTTPS/SSL)結合使用時才被認為是安全的。
2.2 OAuth2
OAuth2 是 REST API 安全的默認標準。它是一個開放的身份驗證和授權標準,允許資源所有者通過訪問令牌授權客户端訪問其私有數據。
2.3 API 密鑰
某些 REST API 使用 API 密鑰進行身份驗證。API 密鑰是一個標識 API 客户端的令牌,而無需引用實際的用户。該令牌可以作為查詢字符串或請求標頭髮送。 類似於基本身份驗證,使用 SSL 可以隱藏密鑰。在本教程中,我們將重點介紹使用 Spring Security 實現 API 密鑰身份驗證。
3. 使用 API 密鑰安全 REST API
本節將創建一個 Spring Boot 應用程序,並使用基於 API 密鑰的身份驗證對其進行安全保護。
3.1. Maven 依賴
讓我們首先在我們的 <em ref="pom.xml"</em> 中聲明 <em ref="org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-security:3.0.6"</em>> 依賴:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>3.2. 創建自定義過濾器
核心思想是從請求中獲取 HTTP API Key 頭部,然後與我們的配置中的密鑰進行驗證。在這種情況下,我們需要在 Spring Security 配置中添加一個自定義過濾器。 我們將首先實現 GenericFilterBean。 GenericFilterBean 是一個 Spring 兼容的 javax.servlet.Filter 實現。 讓我們創建一個 AuthenticationFilter 類:
public class AuthenticationFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
try {
Authentication authentication = AuthenticationService.getAuthentication((HttpServletRequest) request);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
} catch (Exception exp) {
HttpServletResponse httpResponse = (HttpServletResponse) response;
httpResponse.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED);
httpResponse.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
PrintWriter writer = httpResponse.getWriter();
writer.print(exp.getMessage());
writer.flush();
writer.close();
}
}
}我們只需要實現一個 doFilter() 方法。在該方法中,我們評估 API Key 頭部,並將生成的 Authentication 對象設置到當前的 SecurityContext 實例中。然後,請求傳遞給剩餘的過濾器進行處理,路由到 DispatcherServlet,最後傳遞到我們的控制器。如果出現問題,我們捕獲 Exception 並返回給調用者,而不繼續執行過濾器鏈。我們委託 API Key 的評估和 Authentication 對象的構建給 AuthenticationService 類:
public class AuthenticationService {
private static final String AUTH_TOKEN_HEADER_NAME = "X-API-KEY";
private static final String AUTH_TOKEN = "Baeldung";
public static Authentication getAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request) {
String apiKey = request.getHeader(AUTH_TOKEN_HEADER_NAME);
if (apiKey == null || !apiKey.equals(AUTH_TOKEN)) {
throw new BadCredentialsException("Invalid API Key");
}
return new ApiKeyAuthentication(apiKey, AuthorityUtils.NO_AUTHORITIES);
}
}在這裏,我們檢查請求是否包含帶有密鑰的 API Key 頭部。如果頭部是 null 或者不等於 secret,則拋出 BadCredentialsException 異常。如果請求包含該頭部,則進行身份驗證,將密鑰添加到安全上下文中,然後將調用傳遞到後續的安全過濾器。我們的 getAuthentication 方法非常簡單——我們比較 API Key 頭部和 secret 與一個靜態值。為了構造 Authentication 對象,我們必須使用 Spring Security 通常採用的相同方法,通過標準身份驗證的方式構建該對象。因此,讓我們擴展 AbstractAuthenticationToken 類並手動觸發身份驗證。
3.3. 擴展 AbstractAuthenticationToken
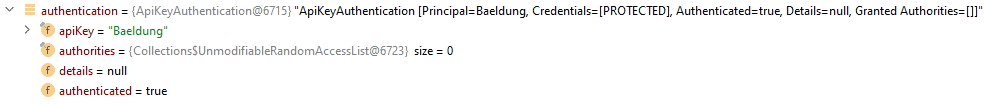
為了成功地為我們的應用程序實現身份驗證,我們需要將傳入的 API 密鑰轉換為一個 Authentication 對象,例如 AbstractAuthenticationToken。 AbstractAuthenticationToken 類實現了 Authentication 接口,代表身份驗證請求的密鑰/主體。 讓我們創建一個 ApiKeyAuthentication 類:
public class ApiKeyAuthentication extends AbstractAuthenticationToken {
private final String apiKey;
public ApiKeyAuthentication(String apiKey, Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
super(authorities);
this.apiKey = apiKey;
setAuthenticated(true);
}
@Override
public Object getCredentials() {
return null;
}
@Override
public Object getPrincipal() {
return apiKey;
}
}ApiKeyAuthentication 類是一種 AbstractAuthenticationToken 類型的對象,它從 HTTP 請求中獲取 apiKey 信息。我們使用構造函數中的 setAuthenticated(true) 方法。因此,Authentication 對象包含 apiKey 和 authenticated 字段:
3.4. 安全配置
我們可以通過創建 SecurityFilterChain 託管自定義過濾器。在這種情況下,我們需要使用 addFilterBefore() 方法在 HttpSecurity 實例上,將 AuthenticationFilter 放置在 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 類之前。 讓我們創建一個 SecurityConfig 類:
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable)
.authorizeHttpRequests(authorizationManagerRequestMatcherRegistry -> authorizationManagerRequestMatcherRegistry.requestMatchers("/**").authenticated())
.httpBasic(Customizer.withDefaults())
.sessionManagement(httpSecuritySessionManagementConfigurer -> httpSecuritySessionManagementConfigurer.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS))
.addFilterBefore(new AuthenticationFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
return http.build();
}
}此外,會話策略設置為 ,因為我們將使用 REST 端點。
3.5. ResourceController
最後,我們將創建一個 ResourceController,併為其定義 /home 映射:
@RestController
public class ResourceController {
@GetMapping("/home")
public String homeEndpoint() {
return "Baeldung !";
}
}3.6. 取消默認自動配置
我們需要禁用默認的安全自動配置。為此,我們排除 <em >SecurityAutoConfiguration</em> 和 <em >UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration</em> 類:
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {SecurityAutoConfiguration.class, UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration.class})
public class ApiKeySecretAuthApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ApiKeySecretAuthApplication.class, args);
}
}現在,該應用程序已準備好進行測試。
4. 測試
我們可以使用 curl 命令來消費受保護的應用。首先,我們嘗試請求 /home,但不提供任何安全憑據:
curl --location --request GET 'http://localhost:8080/home'我們收到了預期的 401 未授權錯誤。現在,讓我們請求相同的資源,但同時提供 API 密鑰和密鑰以進行訪問:
curl --location --request GET 'http://localhost:8080/home' \
--header 'X-API-KEY: Baeldung'因此,服務器的響應是 200 OK。